پیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف — به زبان ساده
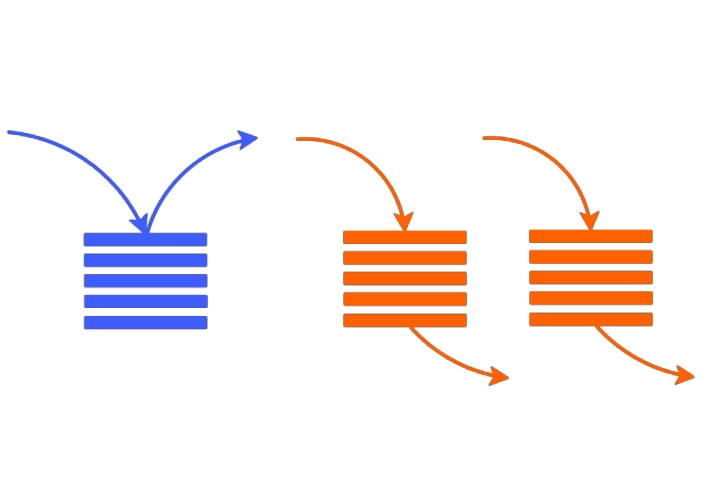
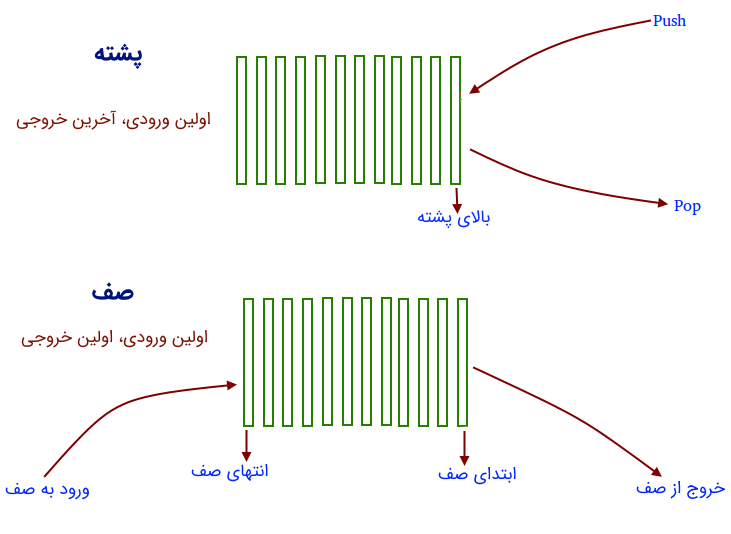
در این مطلب، چگونگی پیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف بیان شده است. یک ساختار داده صف موجود است که از عملیات استانداردی مانند ()enqueue و ()dequeue پشتیبانی میکند. نیاز به پیادهسازی ساختار داده «پشته» (Stack) با استفاده از صف و عملیات آن است. باید توجه داشت که امکان پیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف، وجود دارد. برای این کار، نیاز به دو صف است.
راهکار اول: پر هزینه کردن عملیات
این روش، اطمینان حاصل میکند که عناصری که جدید به پشته وارد شدهاند، همیشه در ابتدای q1 قرار دارند، بنابراین، از عملیات pop فقط در صف q1 استفاده میشود. صف q2 برای قرار دادن هر عنصر جدید در جلوی q1 مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد.
- مراحل عملیات (push(s,x در ادامه بیان شدهاند.
- x را در صف q2 قرار بده.
- همه چیز را یک به یک از q1 خالی کن و در q2 قرار بده.
- نام q1 و q2 را جا به جا کن.
- عملیات (pop(s در ادامه بیان شده است.
- یک عنصر را از q۱ خارج کن و آن را بازگردان.
در ادامه، پیادهسازی رویکرد بالا، در زبانهای برنامهنویسی گوناگون شامل ++C، «جاوا» (Java)، «پایتون» (Python) و «سیشارپ» (#C) انجام شده است.
پیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف در ++C
1/* Program to implement a stack using
2two queue */
3#include<bits/stdc++.h>
4
5using namespace std;
6
7class Stack
8{
9 // Two inbuilt queues
10 queue<int> q1, q2;
11
12 // To maintain current number of
13 // elements
14 int curr_size;
15
16 public:
17 Stack()
18 {
19 curr_size = 0;
20 }
21
22 void push(int x)
23 {
24 curr_size++;
25
26 // Push x first in empty q2
27 q2.push(x);
28
29 // Push all the remaining
30 // elements in q1 to q2.
31 while (!q1.empty())
32 {
33 q2.push(q1.front());
34 q1.pop();
35 }
36
37 // swap the names of two queues
38 queue<int> q = q1;
39 q1 = q2;
40 q2 = q;
41 }
42
43 void pop(){
44
45 // if no elements are there in q1
46 if (q1.empty())
47 return ;
48 q1.pop();
49 curr_size--;
50 }
51
52 int top()
53 {
54 if (q1.empty())
55 return -1;
56 return q1.front();
57 }
58
59 int size()
60 {
61 return curr_size;
62 }
63};
64
65// Driver code
66int main()
67{
68 Stack s;
69 s.push(1);
70 s.push(2);
71 s.push(3);
72
73 cout << "current size: " << s.size()
74 << endl;
75 cout << s.top() << endl;
76 s.pop();
77 cout << s.top() << endl;
78 s.pop();
79 cout << s.top() << endl;
80
81 cout << "current size: " << s.size()
82 << endl;
83 return 0;
84}
85// This code is contributed by Chhaviپیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف در جاوا
1/* Java Program to implement a stack using
2two queue */
3import java.util.*;
4
5class GfG {
6
7static class Stack
8{
9 // Two inbuilt queues
10 static Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
11 static Queue<Integer> q2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
12
13 // To maintain current number of
14 // elements
15 static int curr_size;
16
17 Stack()
18 {
19 curr_size = 0;
20 }
21
22 static void push(int x)
23 {
24 curr_size++;
25
26 // Push x first in empty q2
27 q2.add(x);
28
29 // Push all the remaining
30 // elements in q1 to q2.
31 while (!q1.isEmpty())
32 {
33 q2.add(q1.peek());
34 q1.remove();
35 }
36
37 // swap the names of two queues
38 Queue<Integer> q = q1;
39 q1 = q2;
40 q2 = q;
41 }
42
43 static void pop(){
44
45 // if no elements are there in q1
46 if (q1.isEmpty())
47 return ;
48 q1.remove();
49 curr_size--;
50 }
51
52 static int top()
53 {
54 if (q1.isEmpty())
55 return -1;
56 return q1.peek();
57 }
58
59 static int size()
60 {
61 return curr_size;
62 }
63};
64
65// driver code
66public static void main(String[] args)
67{
68 Stack s = new Stack();
69 s.push(1);
70 s.push(2);
71 s.push(3);
72
73 System.out.println("current size: " + s.size());
74 System.out.println(s.top());
75 s.pop();
76 System.out.println(s.top());
77 s.pop();
78 System.out.println(s.top());
79
80 System.out.println("current size: " + s.size());
81}
82}
83// This code is contributed by Prerna پیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف در پایتون ۳
1# Program to implement a stack using
2# two queue
3from queue import Queue
4
5class Stack:
6
7 def __init__(self):
8
9 # Two inbuilt queues
10 self.q1 = Queue()
11 self.q2 = Queue()
12
13 # To maintain current number
14 # of elements
15 self.curr_size = 0
16
17 def push(self, x):
18 self.curr_size += 1
19
20 # Push x first in empty q2
21 self.q2.put(x)
22
23 # Push all the remaining
24 # elements in q1 to q2.
25 while (not self.q1.empty()):
26 self.q2.put(self.q1.queue[0])
27 self.q1.get()
28
29 # swap the names of two queues
30 self.q = self.q1
31 self.q1 = self.q2
32 self.q2 = self.q
33
34 def pop(self):
35
36 # if no elements are there in q1
37 if (self.q1.empty()):
38 return
39 self.q1.get()
40 self.curr_size -= 1
41
42 def top(self):
43 if (self.q1.empty()):
44 return -1
45 return self.q1.queue[0]
46
47 def size(self):
48 return self.curr_size
49
50# Driver Code
51if __name__ == '__main__':
52 s = Stack()
53 s.push(1)
54 s.push(2)
55 s.push(3)
56
57 print("current size: ", s.size())
58 print(s.top())
59 s.pop()
60 print(s.top())
61 s.pop()
62 print(s.top())
63
64 print("current size: ", s.size())
65
66# This code is contributed by PranchalKپیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف در #C
1/* C# Program to implement a stack using
2two queue */
3using System;
4using System.Collections;
5
6class GfG
7{
8
9public class Stack
10{
11 // Two inbuilt queues
12 public Queue q1 = new Queue();
13 public Queue q2 = new Queue();
14
15 // To maintain current number of
16 // elements
17 public int curr_size;
18
19 public Stack()
20 {
21 curr_size = 0;
22 }
23
24 public void push(int x)
25 {
26 curr_size++;
27
28 // Push x first in empty q2
29 q2.Enqueue(x);
30
31 // Push all the remaining
32 // elements in q1 to q2.
33 while (q1.Count > 0)
34 {
35 q2.Enqueue(q1.Peek());
36 q1.Dequeue();
37 }
38
39 // swap the names of two queues
40 Queue q = q1;
41 q1 = q2;
42 q2 = q;
43 }
44
45 public void pop()
46 {
47
48 // if no elements are there in q1
49 if (q1.Count == 0)
50 return ;
51 q1.Dequeue();
52 curr_size--;
53 }
54
55 public int top()
56 {
57 if (q1.Count == 0)
58 return -1;
59 return (int)q1.Peek();
60 }
61
62 public int size()
63 {
64 return curr_size;
65 }
66};
67
68// Driver code
69public static void Main(String []args)
70{
71 Stack s = new Stack();
72 s.push(1);
73 s.push(2);
74 s.push(3);
75 Console.WriteLine("current size: " + s.size());
76 Console.WriteLine(s.top());
77 s.pop();
78 Console.WriteLine(s.top());
79 s.pop();
80 Console.WriteLine(s.top());
81 Console.WriteLine("current size: " + s.size());
82}
83}
84
85// This code is contributed by Arnab Kunduخروجی قطعه کدهای بالا به صورت زیر است.
current size: 3 3 2 1 current size: 1
روش دوم: پر هزینه کردن عملیات POP
در عمل Push، عنصر جدید همیشه در صف q1 قرار میگیرد. در عملیات ()pop، اگر q2 خالی باشد، همه عناصر به جز آخرین عنصر، به q2 انتقال پیدا میکنند. در نهایت، آخرین عنصر از صف q1 خارج و بازگردانده میشود.
- عملیات (push(s, x
- x را در صف q1 قرار بده (فرض میشود که سایز q1 نامحدود است).
- عملیات (pop(s
- یک به یک عناصر موجود در صف q1، به جز آخرین عنصر را خالی کن و در q2 قرار بده.
- آخرین عنصر از q1 را خارج کن؛ عنصر خارج شده، نتیجه است. آن را ذخیره کن.
- عنصر ذخیره شده در گام قبلی را بازگردان.
پیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف در ++C
1/* Program to implement a stack
2using two queue */
3#include<bits/stdc++.h>
4using namespace std;
5
6class Stack
7{
8 queue<int> q1, q2;
9 int curr_size;
10
11 public:
12 Stack()
13 {
14 curr_size = 0;
15 }
16
17 void pop()
18 {
19 if (q1.empty())
20 return;
21
22 // Leave one element in q1 and
23 // push others in q2.
24 while (q1.size() != 1)
25 {
26 q2.push(q1.front());
27 q1.pop();
28 }
29
30 // Pop the only left element
31 // from q1
32 q1.pop();
33 curr_size--;
34
35 // swap the names of two queues
36 queue<int> q = q1;
37 q1 = q2;
38 q2 = q;
39 }
40
41 void push(int x)
42 {
43 q1.push(x);
44 curr_size++;
45 }
46
47 int top()
48 {
49 if (q1.empty())
50 return -1;
51
52 while( q1.size() != 1 )
53 {
54 q2.push(q1.front());
55 q1.pop();
56 }
57
58 // last pushed element
59 int temp = q1.front();
60
61 // to empty the auxiliary queue after
62 // last operation
63 q1.pop();
64
65 // push last element to q2
66 q2.push(temp);
67
68 // swap the two queues names
69 queue<int> q = q1;
70 q1 = q2;
71 q2 = q;
72 return temp;
73 }
74
75 int size()
76 {
77 return curr_size;
78 }
79};
80
81// Driver code
82int main()
83{
84 Stack s;
85 s.push(1);
86 s.push(2);
87 s.push(3);
88 s.push(4);
89
90 cout << "current size: " << s.size()
91 << endl;
92 cout << s.top() << endl;
93 s.pop();
94 cout << s.top() << endl;
95 s.pop();
96 cout << s.top() << endl;
97 cout << "current size: " << s.size()
98 << endl;
99 return 0;
100}
101// This code is contributed by Chhaviپیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف در جاوا
1/* Java Program to implement a stack
2using two queue */
3import java.util.*;
4
5class Stack
6{
7 Queue<Integer> q1 = new LinkedList<>(), q2 = new LinkedList<>();
8 int curr_size;
9
10 public Stack()
11 {
12 curr_size = 0;
13 }
14
15 void remove()
16 {
17 if (q1.isEmpty())
18 return;
19
20 // Leave one element in q1 and
21 // push others in q2.
22 while (q1.size() != 1)
23 {
24 q2.add(q1.peek());
25 q1.remove();
26 }
27
28 // Pop the only left element
29 // from q1
30 q1.remove();
31 curr_size--;
32
33 // swap the names of two queues
34 Queue<Integer> q = q1;
35 q1 = q2;
36 q2 = q;
37 }
38
39 void add(int x)
40 {
41 q1.add(x);
42 curr_size++;
43 }
44
45 int top()
46 {
47 if (q1.isEmpty())
48 return -1;
49
50 while( q1.size() != 1 )
51 {
52 q2.add(q1.peek());
53 q1.remove();
54 }
55
56 // last pushed element
57 int temp = q1.peek();
58
59 // to empty the auxiliary queue after
60 // last operation
61 q1.remove();
62
63 // push last element to q2
64 q2.add(temp);
65
66 // swap the two queues names
67 Queue<Integer> q = q1;
68 q1 = q2;
69 q2 = q;
70 return temp;
71 }
72
73 int size()
74 {
75 return curr_size;
76 }
77
78// Driver code
79public static void main(String[] args)
80{
81 Stack s = new Stack();
82 s.add(1);
83 s.add(2);
84 s.add(3);
85 s.add(4);
86
87 System.out.println("current size: " + s.size());
88 System.out.println(s.top() );
89 s.remove();
90 System.out.println(s.top() );
91 s.remove();
92 System.out.println(s.top() );
93 System.out.println("current size: " +s.size());
94}
95}
96
97// This code is contributed by Princi Singhپیاده سازی پشته با استفاده از صف در #C
1using System;
2using System.Collections;
3class GfG
4{
5 public class Stack
6 {
7 public Queue q1 = new Queue();
8 public Queue q2 = new Queue();
9 //Just enqueue the new element to q1
10 public void Push(int x) => q1.Enqueue(x);
11
12 //move all elements from q1 to q2 except the rear of q1.
13 //Store the rear of q1
14 //swap q1 and q2
15 //return the stored result
16 public int Pop()
17 {
18 if (q1.Count == 0)
19 return -1;
20 while (q1.Count > 1)
21 {
22 q2.Enqueue(q1.Dequeue());
23 }
24 int res = (int)q1.Dequeue();
25 Queue temp = q1;
26 q1 = q2;
27 q2 = temp;
28 return res;
29 }
30
31 public int Size() => q1.Count;
32
33 public int Top()
34 {
35 if (q1.Count == 0)
36 return -1;
37 while (q1.Count > 1)
38 {
39 q2.Enqueue(q1.Dequeue());
40 }
41 int res = (int)q1.Dequeue();
42 q2.Enqueue(res);
43 Queue temp = q1;
44 q1 = q2;
45 q2 = temp;
46 return res;
47 }
48 };
49 public static void Main(String[] args)
50 {
51 Stack s = new Stack();
52 s.Push(1);
53 Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: " + s.Size() + "\tTop : " + s.Top());
54 s.Push(7);
55 Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: " + s.Size() + "\tTop : " + s.Top());
56 s.Push(9);
57 Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: " + s.Size() + "\tTop : " + s.Top());
58
59 s.Pop();
60 Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: " + s.Size() + "\tTop : " + s.Top());
61 s.Pop();
62 Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: " + s.Size() + "\tTop : " + s.Top());
63
64 s.Push(5);
65 Console.WriteLine("Size of Stack: " + s.Size() + "\tTop : " + s.Top());
66 }
67}
68//Submitted by Sakti Prasad
69
70//Size of Stack: 1 Top : 1
71//Size of Stack: 2 Top : 7
72//Size of Stack: 3 Top : 9
73//Size of Stack: 2 Top : 7
74//Size of Stack: 1 Top : 1
75//Size of Stack: 2 Top : 5خروجی قطعه کدهای بالا، به صورت زیر است.
current size: 4 4 3 2 current size: 2
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- آموزش برنامهنویسی C++
- مجموعه آموزشهای ریاضیات
- یافتن دور همیلتونی با الگوریتم پس گرد — به زبان ساده
- الگوریتم بازی مار و پله همراه با کد — به زبان ساده
- حل مساله n وزیر با الگوریتم پسگرد (Backtracking) — به زبان ساده
^^