الگوریتم بازی مار و پله همراه با کد — به زبان ساده
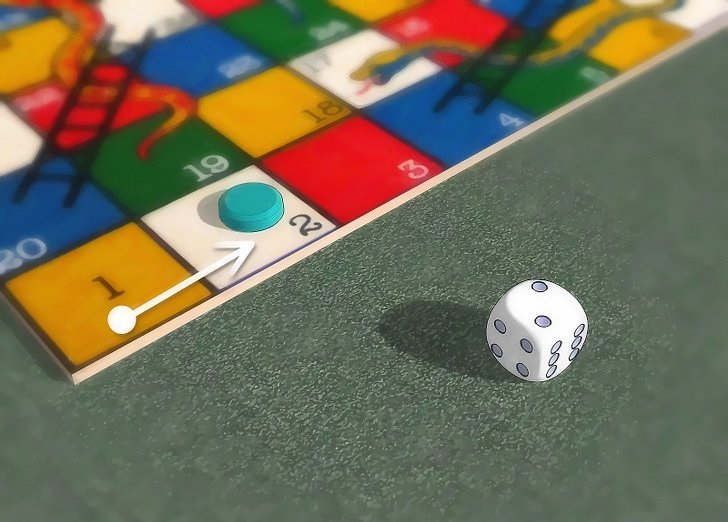

بازی مار و پله (Snakes and Ladders)، یک بازی باستانی هندی است که اکنون یک بازی کلاسیک جهانی محبوب محسوب میشود. این بازی قابل انجام بین دو یا تعداد بیشتری بازیکن است. صفحه بازی مار و پله، شطرنجی است؛ در این بازی، در برخی از خانهها نردبانهایی وجود دارد که فرد را به خانههای بالاتر میرساند و در بعضی از خانهها، مارهایی وجود دارد که فرد را اصطلاحا نیش میزنند و به خانههای پایینتری انتقال میدهند (جایی که دم مار در آن قرار دارد). بازی به این صورت انجام میشود که هر بازیکن تاس میاندازد و با توجه به عددی که میآید، تعداد خانههایی را به جلو حرکت میکند. بسته به عدد تاس، ممکن است فرد در یک خانه عادی، دارای نربان و یا دارای مار قرار بگیرد. در «مساله مار و پله» (Snake and Ladder Problem)، هدف پیدا کردن کمترین تعداد دفعات پرتاب تاس لازم برای رسیدن به مقصد (آخرین خانه در صفحه شطرنجی) از مبدا (اولین خانه) است. این مساله کمی با بازی تختهای متداول مار و پله که افراد بازی میکنند متفاوت است و در آن، بازیکن بر عددی که در پرتاب تاس به دست میآید کنترل دارد و باید اعدادی را پیدا کند که با کمترین تعداد پرتاب تاس به خانه نهایی برسد. در ادامه، الگوریتم بازی مار و پله (در واقع الگوریتم لازم برای حل این مساله) ارائه و پیادهسازی آن در زبانهای برنامهنویسی «پایتون» (Python)، «جاوا» (Java)، «سیپلاسپلاس» (++C) و «سیشارپ» (#C) انجام شده است.
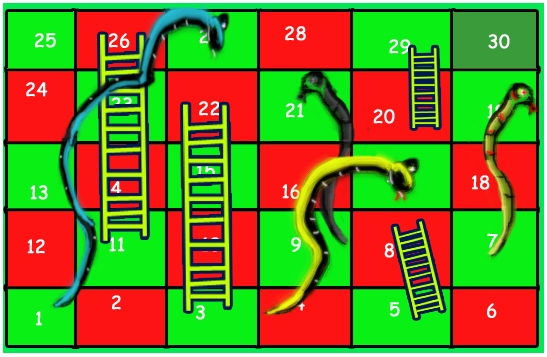
الگوریتم بازی مار و پله
برای مثال، در صفحه بازی موجود در تصویر بالا، تعداد پرتابهای تاس لازم برای رسیدن از خانه ۱ به خانه ۳۰ برابر با سه است. گامهای زیر برای آنکه بازیکن با سه پرتاب تاس به نتیجه برسد انجام میشود.
- ابتدا تاس دو انداخته میشود تا بازیکن از خانه یک به خانه سه برود و با استفاده از نردبان به خانه ۲۲ برسد.
- سپس، تاس ۶ انداخته میشود تا فرد از خانه ۲۲ به خانه ۲۸ برسد.
- در نهایت، با انداختن تاس ۲، بازیکن به خانه ۳۰ (مقصد نهایی) میرسد.
برخی از دیگر راهکارهای موجود برای حل مساله مار و پله (با کمترین تعداد پرتاب تاس) عبارتند از: (2, 2, 6)، (2, 4, 4) و (2, 3, 5).
ایده موجود برای حل این مساله در حالت کلی آن است که صفحه بازی به صورت یک گراف جهتدار در نظر گرفته شود. اکنون، مساله یافتن کوتاهترین مسیر در گراف است. هر «راس» (Vertex) از گراف، دارای «یالی» (Edge) به شش راس بعدی است؛ اگر راسهای بعدی دارای نردبان یا مار نباشند. اگر هر یک از شش راس دارای مار یا نردبان باشند، یال از راس کنونی به راس بالای نردبان یا دم مار متصل میشود.
با توجه به اینکه همه یالها دارای وزنهای برابری هستند، میتوان کوتاهترین مسیر را با استفاده از «جستجوی اول عمق» (Breadth First Search) کشف کرد. در ادامه، پیادهسازی ایده بالا با استفاده از زبانهای برنامهنویسی گوناگون انجام شده است. ورودی با دو چیز نمایش داده شده است: N که تعداد خانههای صفحه بازی است و آرایه [move[0…N-1 با اندازه N. یک ورودی [move[i برابر با ۱- است اگر هیچ مار یا نردبانی از i وجود نداشته باشد؛ در غیر این صورت، [move[i حاوی اندیس سلول مقصد برای مار یا نردبان در i است.
پیاده سازی الگوریتم بازی مار و پله در ++C
1// C++ program to find minimum number of dice throws required to
2// reach last cell from first cell of a given snake and ladder
3// board
4#include<iostream>
5#include <queue>
6using namespace std;
7
8// An entry in queue used in BFS
9struct queueEntry
10{
11 int v; // Vertex number
12 int dist; // Distance of this vertex from source
13};
14
15// This function returns minimum number of dice throws required to
16// Reach last cell from 0'th cell in a snake and ladder game.
17// move[] is an array of size N where N is no. of cells on board
18// If there is no snake or ladder from cell i, then move[i] is -1
19// Otherwise move[i] contains cell to which snake or ladder at i
20// takes to.
21int getMinDiceThrows(int move[], int N)
22{
23 // The graph has N vertices. Mark all the vertices as
24 // not visited
25 bool *visited = new bool[N];
26 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
27 visited[i] = false;
28
29 // Create a queue for BFS
30 queue<queueEntry> q;
31
32 // Mark the node 0 as visited and enqueue it.
33 visited[0] = true;
34 queueEntry s = {0, 0}; // distance of 0't vertex is also 0
35 q.push(s); // Enqueue 0'th vertex
36
37 // Do a BFS starting from vertex at index 0
38 queueEntry qe; // A queue entry (qe)
39 while (!q.empty())
40 {
41 qe = q.front();
42 int v = qe.v; // vertex no. of queue entry
43
44 // If front vertex is the destination vertex,
45 // we are done
46 if (v == N-1)
47 break;
48
49 // Otherwise dequeue the front vertex and enqueue
50 // its adjacent vertices (or cell numbers reachable
51 // through a dice throw)
52 q.pop();
53 for (int j=v+1; j<=(v+6) && j<N; ++j)
54 {
55 // If this cell is already visited, then ignore
56 if (!visited[j])
57 {
58 // Otherwise calculate its distance and mark it
59 // as visited
60 queueEntry a;
61 a.dist = (qe.dist + 1);
62 visited[j] = true;
63
64 // Check if there a snake or ladder at 'j'
65 // then tail of snake or top of ladder
66 // become the adjacent of 'i'
67 if (move[j] != -1)
68 a.v = move[j];
69 else
70 a.v = j;
71 q.push(a);
72 }
73 }
74 }
75
76 // We reach here when 'qe' has last vertex
77 // return the distance of vertex in 'qe'
78 return qe.dist;
79}
80
81// Driver program to test methods of graph class
82int main()
83{
84 // Let us construct the board given in above diagram
85 int N = 30;
86 int moves[N];
87 for (int i = 0; i<N; i++)
88 moves[i] = -1;
89
90 // Ladders
91 moves[2] = 21;
92 moves[4] = 7;
93 moves[10] = 25;
94 moves[19] = 28;
95
96 // Snakes
97 moves[26] = 0;
98 moves[20] = 8;
99 moves[16] = 3;
100 moves[18] = 6;
101
102 cout << "Min Dice throws required is " << getMinDiceThrows(moves, N);
103 return 0;
104}پیاده سازی الگوریتم بازی مار و پله در پایتون
1# Python3 program to find minimum number
2# of dice throws required to reach last
3# cell from first cell of a given
4# snake and ladder board
5
6# An entry in queue used in BFS
7class QueueEntry(object):
8 def __init__(self, v = 0, dist = 0):
9 self.v = v
10 self.dist = dist
11
12'''This function returns minimum number of
13dice throws required to. Reach last cell
14from 0'th cell in a snake and ladder game.
15move[] is an array of size N where N is
16no. of cells on board. If there is no
17snake or ladder from cell i, then move[i]
18is -1. Otherwise move[i] contains cell to
19which snake or ladder at i takes to.'''
20def getMinDiceThrows(move, N):
21
22 # The graph has N vertices. Mark all
23 # the vertices as not visited
24 visited = [False] * N
25
26 # Create a queue for BFS
27 queue = []
28
29 # Mark the node 0 as visited and enqueue it
30 visited[0] = True
31
32 # Distance of 0't vertex is also 0
33 # Enqueue 0'th vertex
34 queue.append(QueueEntry(0, 0))
35
36 # Do a BFS starting from vertex at index 0
37 qe = QueueEntry() # A queue entry (qe)
38 while queue:
39 qe = queue.pop(0)
40 v = qe.v # Vertex no. of queue entry
41
42 # If front vertex is the destination
43 # vertex, we are done
44 if v == N - 1:
45 break
46
47 # Otherwise dequeue the front vertex
48 # and enqueue its adjacent vertices
49 # (or cell numbers reachable through
50 # a dice throw)
51 j = v + 1
52 while j <= v + 6 and j < N:
53
54 # If this cell is already visited,
55 # then ignore
56 if visited[j] is False:
57
58 # Otherwise calculate its
59 # distance and mark it
60 # as visited
61 a = QueueEntry()
62 a.dist = qe.dist + 1
63 visited[j] = True
64
65 # Check if there a snake or ladder
66 # at 'j' then tail of snake or top
67 # of ladder become the adjacent of 'i'
68 a.v = move[j] if move[j] != -1 else j
69
70 queue.append(a)
71
72 j += 1
73
74 # We reach here when 'qe' has last vertex
75 # return the distance of vertex in 'qe
76 return qe.dist
77
78# driver code
79N = 30
80moves = [-1] * N
81
82# Ladders
83moves[2] = 21
84moves[4] = 7
85moves[10] = 25
86moves[19] = 28
87
88# Snakes
89moves[26] = 0
90moves[20] = 8
91moves[16] = 3
92moves[18] = 6
93
94print("Min Dice throws required is {0}".
95 format(getMinDiceThrows(moves, N)))
96
97# This code is contributed by Ajitesh Pathakپیاده سازی الگوریتم بازی مار و پله در جاوا
1// Java program to find minimum number of dice
2// throws required to reach last cell from first
3// cell of a given snake and ladder board
4
5import java.util.LinkedList;
6import java.util.Queue;
7
8public class SnakesLadder
9{
10 // An entry in queue used in BFS
11 static class qentry
12 {
13 int v;// Vertex number
14 int dist;// Distance of this vertex from source
15 }
16
17 // This function returns minimum number of dice
18 // throws required to Reach last cell from 0'th cell
19 // in a snake and ladder game. move[] is an array of
20 // size N where N is no. of cells on board If there
21 // is no snake or ladder from cell i, then move[i]
22 // is -1 Otherwise move[i] contains cell to which
23 // snake or ladder at i takes to.
24 static int getMinDiceThrows(int move[], int n)
25 {
26 int visited[] = new int[n];
27 Queue<qentry> q = new LinkedList<>();
28 qentry qe = new qentry();
29 qe.v = 0;
30 qe.dist = 0;
31
32 // Mark the node 0 as visited and enqueue it.
33 visited[0] = 1;
34 q.add(qe);
35
36 // Do a BFS starting from vertex at index 0
37 while (!q.isEmpty())
38 {
39 qe = q.remove();
40 int v = qe.v;
41
42 // If front vertex is the destination
43 // vertex, we are done
44 if (v == n - 1)
45 break;
46
47 // Otherwise dequeue the front vertex and
48 // enqueue its adjacent vertices (or cell
49 // numbers reachable through a dice throw)
50 for (int j = v + 1; j <= (v + 6) && j < n; ++j)
51 {
52 // If this cell is already visited, then ignore
53 if (visited[j] == 0)
54 {
55 // Otherwise calculate its distance and
56 // mark it as visited
57 qentry a = new qentry();
58 a.dist = (qe.dist + 1);
59 visited[j] = 1;
60
61 // Check if there a snake or ladder at 'j'
62 // then tail of snake or top of ladder
63 // become the adjacent of 'i'
64 if (move[j] != -1)
65 a.v = move[j];
66 else
67 a.v = j;
68 q.add(a);
69 }
70 }
71 }
72
73 // We reach here when 'qe' has last vertex
74 // return the distance of vertex in 'qe'
75 return qe.dist;
76 }
77
78 public static void main(String[] args)
79 {
80 // Let us construct the board given in above diagram
81 int N = 30;
82 int moves[] = new int[N];
83 for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
84 moves[i] = -1;
85
86 // Ladders
87 moves[2] = 21;
88 moves[4] = 7;
89 moves[10] = 25;
90 moves[19] = 28;
91
92 // Snakes
93 moves[26] = 0;
94 moves[20] = 8;
95 moves[16] = 3;
96 moves[18] = 6;
97
98 System.out.println("Min Dice throws required is " +
99 getMinDiceThrows(moves, N));
100 }
101}خروجی:
Min Dice throws required is 3
پیچیدگی زمانی راهکار بالا از درجه (O(N است؛ زیرا هر سلول تنها یکبار به «صف» (Queue) اضافه و کم میشود و یک فرایند معمول افزودن به صف یا حذف کردن از آن از درجه زمانی (O(1 است.
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامه نویسی
- آموزش ساختمان دادهها
- مجموعه آموزشهای ساختمان داده و طراحی الگوریتم
- زبان برنامهنویسی پایتون (Python) — از صفر تا صد
- آموزش ساختمان داده — مجموعه مقالات جامع وبلاگ فرادرس
^^










جاوااسکریپت نیست ؟
سلام وقت بخیر و خسته نباشید به شما استاد گرامی
اگه امکانش باشه با بیسیک فور اندروید هم کدش رو قرار بدین
با تشکر