حل مساله بیشینه جریان — راهنمای جامع

در این مطلب، روش حل مساله بیشینه جریان (Maximum Flow Problem) بیان و راهکار بیان شده برای آن در زبانهای برنامهنویسی گوناگون شامل «سیپلاسپلاس» (++C)، «جاوا» (Java)، «پایتون» (Python) و «سیشارپ» (#C) پیادهسازی شده است. یک گراف داده شده که نشانگر یک «شبکه جریان» (Flow Network) است و در آن، هر «یال» (Edge) دارای ظرفیت است. همچنین، دو راس s (مبدا | Source) و t (مقصد | Sink) در گراف داده شده است. هدف پیدا کردن بیشینه جریان ممکنی است که از s به t با در نظر داشتن محدودیتهای زیر، شکل میگیرد.
- جریان روی یک یال از ظرفیت داده شده روی آن یال سر ریز نمیکند.
- جریان ورودی برای هر راس، به جز s و t، مساوی با جریان خروجی است.
برای مثال، میتوان گراف زیر را در نظر گرفت.
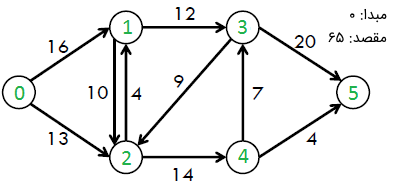
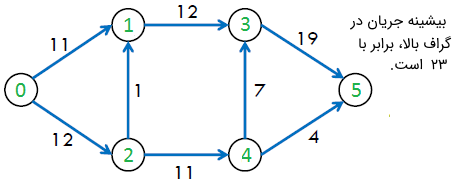
بیشینه جریان ممکن در گراف بالا برابر با ۲۳ است.
الگوریتم فورد–فالکرسون برای حل مساله بیشینه جریان
در ادامه، «الگوریتم فورد–فالکرسون» (Ford-Fulkerson Algorithm) برای حل مساله بیشینه جریان ارائه شده است.
- با جریان اولیه ۰ شروع کن.
- تا هنگامی که یک مسیر تجمعی از مبدا به مقصد وجود دارد، این «مسیر-جریان» (Path-Flow) را به «جریان» اضافه کن.
- جریان را بازگردان.
پیچیدگی زمانی الگوریتم بالا از درجه O(max_flow * E) است. هنگامی که یک مسیر تجمعی وجود داشته باشد، یک حلقه اجرا میشود. در بدترین حالت، ممکن است ۱ واحد جریان در هر تکرار اضافه شود. بنابراین، پیچیدگی زمانی برابر با O(max_flow * E) خواهد شد.
پیادهسازی الگوریتم ساده بالا
برای پیادهسازی الگوریتم بالا، ابتدا باید مفهوم «گراف باقیمانده» (Residual Graph) تعریف شود که برای درک این پیادهسازی مورد نیاز است. گراف باقیمانده از یک شبکه جریان، گرافی است که جریان اضافی ممکن را نشان میدهد. اگر مسیری از مبدا به مقصد وجود داشته باشد، این امکان وجود دارد که جریان اضافه شود. هر یال از گراف دارای مقداری است که به آن ظرفیت باقیمانده گفته میشود. ظرفیت باقیمانده برابر با ظرفیت اصلی یالها منهای جریان کنونی است. ظرفیت باقیمانده اساسا ظرفیت کنونی یالها است.
اکنون، پیرامون جزئیات پیادهسازی صحبت خواهد شد. اگر هیچ یالی بین دو راس از گراف باقیمانده وجود نداشته باشد، ظرفیت باقیمانده برابر با ۰ است. میتوان با توجه به اینکه هیچ جریان اولیهای وجود ندارد، به گراف باقیمانده مقداردهی اولیه کرد. همچنین، ظرفیت باقیمانده اولیه برابر با ظرفیت اصلی است. برای پیدا کردن مسیر تجمعی، میتوان از الگوریتم «جستجوی اول سطح» (Breadth-First Search) یا «جستجوی اول عمق» (Depth-First Search) استفاده کرد. در پیادهسازی زیر، برای پیدا کردن مسیر تجمعی از BFS استفاده شده است.
با استفاده از BFS، میتوان بررسی کرد که آیا مسیری از مبدا به مقصد وجود دارد یا خیر. همچنین، BFS، آرایه parent[] را میسازد. با استفاده از آرایه parent[]، پیمایش در مسیر یافته شده انجام و جریان احتمالی از طریق این مسیر با پیدا کردن ظرفیت باقیمانده در طول مسیر پیدا میشود. در ادامه، جریان مسیر یافت شده به جریان کلی اضافه میشود. نکته مهم آن است که به روز رسانی ظرفیت باقیماندهها در گراف باقیمانده مورد نیاز است. جریان مسیر از همه یالها در طول مسیر کسر میشود و جریان مسیر در امتداد یالهای معکوس اضافه میشود. نیاز به اضافه کردن جریان مسیر در طول یالهای معکوس است، زیرا ممکن است بعدا نیاز به ارسال جریان در جهت معکوس باشد.
حل مساله بیشینه جریان در ++C
1// C++ program for implementation of Ford Fulkerson algorithm
2#include <iostream>
3#include <limits.h>
4#include <string.h>
5#include <queue>
6using namespace std;
7
8// Number of vertices in given graph
9#define V 6
10
11/* Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink 't' in
12 residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path */
13bool bfs(int rGraph[V][V], int s, int t, int parent[])
14{
15 // Create a visited array and mark all vertices as not visited
16 bool visited[V];
17 memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
18
19 // Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark source vertex
20 // as visited
21 queue <int> q;
22 q.push(s);
23 visited[s] = true;
24 parent[s] = -1;
25
26 // Standard BFS Loop
27 while (!q.empty())
28 {
29 int u = q.front();
30 q.pop();
31
32 for (int v=0; v<V; v++)
33 {
34 if (visited[v]==false && rGraph[u][v] > 0)
35 {
36 q.push(v);
37 parent[v] = u;
38 visited[v] = true;
39 }
40 }
41 }
42
43 // If we reached sink in BFS starting from source, then return
44 // true, else false
45 return (visited[t] == true);
46}
47
48// Returns the maximum flow from s to t in the given graph
49int fordFulkerson(int graph[V][V], int s, int t)
50{
51 int u, v;
52
53 // Create a residual graph and fill the residual graph with
54 // given capacities in the original graph as residual capacities
55 // in residual graph
56 int rGraph[V][V]; // Residual graph where rGraph[i][j] indicates
57 // residual capacity of edge from i to j (if there
58 // is an edge. If rGraph[i][j] is 0, then there is not)
59 for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
60 for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
61 rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
62
63 int parent[V]; // This array is filled by BFS and to store path
64
65 int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
66
67 // Augment the flow while tere is path from source to sink
68 while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent))
69 {
70 // Find minimum residual capacity of the edges along the
71 // path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the maximum flow
72 // through the path found.
73 int path_flow = INT_MAX;
74 for (v=t; v!=s; v=parent[v])
75 {
76 u = parent[v];
77 path_flow = min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
78 }
79
80 // update residual capacities of the edges and reverse edges
81 // along the path
82 for (v=t; v != s; v=parent[v])
83 {
84 u = parent[v];
85 rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
86 rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
87 }
88
89 // Add path flow to overall flow
90 max_flow += path_flow;
91 }
92
93 // Return the overall flow
94 return max_flow;
95}
96
97// Driver program to test above functions
98int main()
99{
100 // Let us create a graph shown in the above example
101 int graph[V][V] = { {0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0},
102 {0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0},
103 {0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0},
104 {0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20},
105 {0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4},
106 {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
107 };
108
109 cout << "The maximum possible flow is " << fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5);
110
111 return 0;
112}حل مساله بیشینه جریان در جاوا
1// Java program for implementation of Ford Fulkerson algorithm
2import java.util.*;
3import java.lang.*;
4import java.io.*;
5import java.util.LinkedList;
6
7class MaxFlow
8{
9 static final int V = 6; //Number of vertices in graph
10
11 /* Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink
12 't' in residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the
13 path */
14 boolean bfs(int rGraph[][], int s, int t, int parent[])
15 {
16 // Create a visited array and mark all vertices as not
17 // visited
18 boolean visited[] = new boolean[V];
19 for(int i=0; i<V; ++i)
20 visited[i]=false;
21
22 // Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark
23 // source vertex as visited
24 LinkedList<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
25 queue.add(s);
26 visited[s] = true;
27 parent[s]=-1;
28
29 // Standard BFS Loop
30 while (queue.size()!=0)
31 {
32 int u = queue.poll();
33
34 for (int v=0; v<V; v++)
35 {
36 if (visited[v]==false && rGraph[u][v] > 0)
37 {
38 queue.add(v);
39 parent[v] = u;
40 visited[v] = true;
41 }
42 }
43 }
44
45 // If we reached sink in BFS starting from source, then
46 // return true, else false
47 return (visited[t] == true);
48 }
49
50 // Returns tne maximum flow from s to t in the given graph
51 int fordFulkerson(int graph[][], int s, int t)
52 {
53 int u, v;
54
55 // Create a residual graph and fill the residual graph
56 // with given capacities in the original graph as
57 // residual capacities in residual graph
58
59 // Residual graph where rGraph[i][j] indicates
60 // residual capacity of edge from i to j (if there
61 // is an edge. If rGraph[i][j] is 0, then there is
62 // not)
63 int rGraph[][] = new int[V][V];
64
65 for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
66 for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
67 rGraph[u][v] = graph[u][v];
68
69 // This array is filled by BFS and to store path
70 int parent[] = new int[V];
71
72 int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
73
74 // Augment the flow while tere is path from source
75 // to sink
76 while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent))
77 {
78 // Find minimum residual capacity of the edhes
79 // along the path filled by BFS. Or we can say
80 // find the maximum flow through the path found.
81 int path_flow = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
82 for (v=t; v!=s; v=parent[v])
83 {
84 u = parent[v];
85 path_flow = Math.min(path_flow, rGraph[u][v]);
86 }
87
88 // update residual capacities of the edges and
89 // reverse edges along the path
90 for (v=t; v != s; v=parent[v])
91 {
92 u = parent[v];
93 rGraph[u][v] -= path_flow;
94 rGraph[v][u] += path_flow;
95 }
96
97 // Add path flow to overall flow
98 max_flow += path_flow;
99 }
100
101 // Return the overall flow
102 return max_flow;
103 }
104
105 // Driver program to test above functions
106 public static void main (String[] args) throws java.lang.Exception
107 {
108 // Let us create a graph shown in the above example
109 int graph[][] =new int[][] { {0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0},
110 {0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0},
111 {0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0},
112 {0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20},
113 {0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4},
114 {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
115 };
116 MaxFlow m = new MaxFlow();
117
118 System.out.println("The maximum possible flow is " +
119 m.fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5));
120
121 }
122} حل مساله بیشینه جریان در پایتون
1# Python program for implementation of Ford Fulkerson algorithm
2
3from collections import defaultdict
4
5#This class represents a directed graph using adjacency matrix representation
6class Graph:
7
8 def __init__(self,graph):
9 self.graph = graph # residual graph
10 self. ROW = len(graph)
11 #self.COL = len(gr[0])
12
13
14 '''Returns true if there is a path from source 's' to sink 't' in
15 residual graph. Also fills parent[] to store the path '''
16 def BFS(self,s, t, parent):
17
18 # Mark all the vertices as not visited
19 visited =[False]*(self.ROW)
20
21 # Create a queue for BFS
22 queue=[]
23
24 # Mark the source node as visited and enqueue it
25 queue.append(s)
26 visited[s] = True
27
28 # Standard BFS Loop
29 while queue:
30
31 #Dequeue a vertex from queue and print it
32 u = queue.pop(0)
33
34 # Get all adjacent vertices of the dequeued vertex u
35 # If a adjacent has not been visited, then mark it
36 # visited and enqueue it
37 for ind, val in enumerate(self.graph[u]):
38 if visited[ind] == False and val > 0 :
39 queue.append(ind)
40 visited[ind] = True
41 parent[ind] = u
42
43 # If we reached sink in BFS starting from source, then return
44 # true, else false
45 return True if visited[t] else False
46
47
48 # Returns tne maximum flow from s to t in the given graph
49 def FordFulkerson(self, source, sink):
50
51 # This array is filled by BFS and to store path
52 parent = [-1]*(self.ROW)
53
54 max_flow = 0 # There is no flow initially
55
56 # Augment the flow while there is path from source to sink
57 while self.BFS(source, sink, parent) :
58
59 # Find minimum residual capacity of the edges along the
60 # path filled by BFS. Or we can say find the maximum flow
61 # through the path found.
62 path_flow = float("Inf")
63 s = sink
64 while(s != source):
65 path_flow = min (path_flow, self.graph[parent[s]][s])
66 s = parent[s]
67
68 # Add path flow to overall flow
69 max_flow += path_flow
70
71 # update residual capacities of the edges and reverse edges
72 # along the path
73 v = sink
74 while(v != source):
75 u = parent[v]
76 self.graph[u][v] -= path_flow
77 self.graph[v][u] += path_flow
78 v = parent[v]
79
80 return max_flow
81
82
83# Create a graph given in the above diagram
84
85graph = [[0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0],
86 [0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0],
87 [0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0],
88 [0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20],
89 [0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4],
90 [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
91
92g = Graph(graph)
93
94source = 0; sink = 5
95
96print ("The maximum possible flow is %d " % g.FordFulkerson(source, sink))
97
98#This code is contributed by Neelam Yadav حل مساله بیشینه جریان در #C
1// C# program for implementation
2// of Ford Fulkerson algorithm
3using System;
4using System.Collections.Generic;
5
6public class MaxFlow
7{
8 static readonly int V = 6; //Number of vertices in graph
9
10 /* Returns true if there is a path
11 from source 's' to sink 't' in residual
12 graph. Also fills parent[] to store the
13 path */
14 bool bfs(int [,]rGraph, int s, int t, int []parent)
15 {
16 // Create a visited array and mark
17 // all vertices as not visited
18 bool []visited = new bool[V];
19 for(int i = 0; i < V; ++i)
20 visited[i] = false;
21
22 // Create a queue, enqueue source vertex and mark
23 // source vertex as visited
24 List<int> queue = new List<int>();
25 queue.Add(s);
26 visited[s] = true;
27 parent[s] = -1;
28
29 // Standard BFS Loop
30 while (queue.Count != 0)
31 {
32 int u = queue[0];
33 queue.RemoveAt(0);
34
35 for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
36 {
37 if (visited[v] == false && rGraph[u, v] > 0)
38 {
39 queue.Add(v);
40 parent[v] = u;
41 visited[v] = true;
42 }
43 }
44 }
45
46 // If we reached sink in BFS
47 // starting from source, then
48 // return true, else false
49 return (visited[t] == true);
50 }
51
52 // Returns tne maximum flow
53 // from s to t in the given graph
54 int fordFulkerson(int [,]graph, int s, int t)
55 {
56 int u, v;
57
58 // Create a residual graph and fill
59 // the residual graph with given
60 // capacities in the original graph as
61 // residual capacities in residual graph
62
63 // Residual graph where rGraph[i,j]
64 // indicates residual capacity of
65 // edge from i to j (if there is an
66 // edge. If rGraph[i,j] is 0, then
67 // there is not)
68 int [,]rGraph = new int[V, V];
69
70 for (u = 0; u < V; u++)
71 for (v = 0; v < V; v++)
72 rGraph[u, v] = graph[u, v];
73
74 // This array is filled by BFS and to store path
75 int []parent = new int[V];
76
77 int max_flow = 0; // There is no flow initially
78
79 // Augment the flow while tere is path from source
80 // to sink
81 while (bfs(rGraph, s, t, parent))
82 {
83 // Find minimum residual capacity of the edhes
84 // along the path filled by BFS. Or we can say
85 // find the maximum flow through the path found.
86 int path_flow = int.MaxValue;
87 for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
88 {
89 u = parent[v];
90 path_flow = Math.Min(path_flow, rGraph[u,v]);
91 }
92
93 // update residual capacities of the edges and
94 // reverse edges along the path
95 for (v = t; v != s; v = parent[v])
96 {
97 u = parent[v];
98 rGraph[u,v] -= path_flow;
99 rGraph[v,u] += path_flow;
100 }
101
102 // Add path flow to overall flow
103 max_flow += path_flow;
104 }
105
106 // Return the overall flow
107 return max_flow;
108 }
109
110 // Driver code
111 public static void Main ()
112 {
113 // Let us create a graph shown in the above example
114 int [,]graph =new int[,] { {0, 16, 13, 0, 0, 0},
115 {0, 0, 10, 12, 0, 0},
116 {0, 4, 0, 0, 14, 0},
117 {0, 0, 9, 0, 0, 20},
118 {0, 0, 0, 7, 0, 4},
119 {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
120 };
121 MaxFlow m = new MaxFlow();
122
123 Console.WriteLine("The maximum possible flow is " +
124 m.fordFulkerson(graph, 0, 5));
125
126 }
127}
128
129/* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */خروجی قطعه کدهای بالا به صورت زیر است.
The maximum possible flow is 23
پیادهسازی بالا از الگوریتم فورد–فالکرسون را «الگوریتم ادموندز کارپ» (Edmonds-Karp Algorithm) میگویند. ایده اصلی نهفته در پس استفاده از الگوریتم ادموندز کارپ، استفاده از BFS است؛ زیرا BFS همیشه مسیری با کمترین تعداد یال را انتخاب میکند.
هنگامی که BFS مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد، پیچیدگی زمانی بدترین حالت را میتوان به O(VE2) کاهش داد. پیادهسازی بالا از ارائه ماتریس مجاورت استفاده میکند و BFS دارای پیچیدگی زمانی از درجه O(V2) است.
این مسأله با توجه به اینکه در بسیاری از موقعیتهای عملی به وقوع میپیوندد، بسیار حائز است. از جمله مثالهایی برای مسأله بیشینه جریان میتوان زد، افزایش حمل و نقل با توجه به محدودیتهای ترافیکی داده شده و افزایش جریان بستهها در شبکههای کامپیوتری است.
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- آموزش ساختمان دادهها
- مجموعه آموزشهای ساختمان داده و طراحی الگوریتم
- یافتن دور همیلتونی با الگوریتم پس گرد — به زبان ساده
- الگوریتم بازی مار و پله همراه با کد — به زبان ساده
- حل مساله n وزیر با الگوریتم پسگرد (Backtracking) — به زبان ساده
^^