آشنایی با Semaphore در جاوا — راهنمای جامع
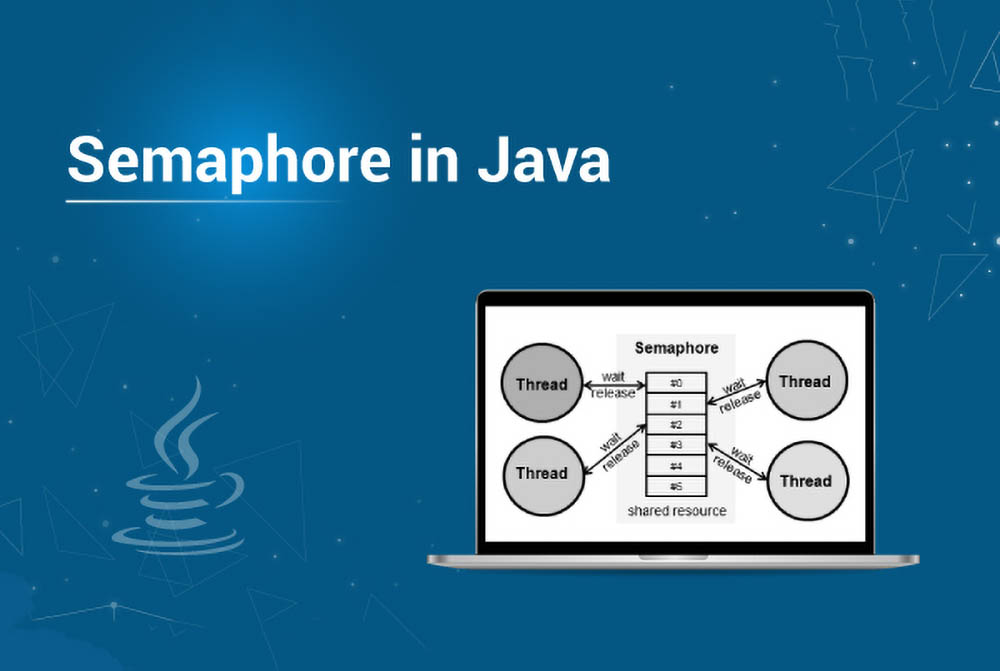
در این راهنمای کوتاه از سری مقالات آموزش جامع جاوا، به بررسی مبانی Semaphore در جاوا و همچنین mutex-ها میپردازیم.
Semaphore چیست؟
توضیح خود را از java.util.concurrent.Semaphore آغاز میکنیم. از Semaphore میتوان برای محدودسازی تعداد نخهایی که به صورت همزمان به یک منبع خاص دسترسی مییابند استفاده کرد.
در مثال زیر، یک صف لاگین ساده برای محدود کردن تعداد کاربران در سیستم پیادهسازی میکنیم:
1
2class LoginQueueUsingSemaphore {
3
4 private Semaphore semaphore;
5
6 public LoginQueueUsingSemaphore(int slotLimit) {
7 semaphore = new Semaphore(slotLimit);
8 }
9
10 boolean tryLogin() {
11 return semaphore.tryAcquire();
12 }
13
14 void logout() {
15 semaphore.release();
16 }
17
18 int availableSlots() {
19 return semaphore.availablePermits();
20 }
21
22}به روش استفاده از متدهای زیر توجه کنید:
- ()tryAcquire – این متد در صورتی که یک مجوز، بیدرنگ موجود باشد، مقدار true بازگشت داده و آن را در اختیار میگیرد، در غیر این صورت مقدار false بازگشت میدهد، اما ()acquire نیازمند یک مجوز است و تا زمانی که چنین مجوزی موجود شود، مسدود میشود.
- ()release – یک مجوز را آزاد میکند.
- ()availablePermits – این متد تعداد مجوزهایی که هم اینک موجود است را بازگشت میدهد.
برای تست صف لاگین، ابتدا باید به محدودیت برسیم و بررسی کنیم آیا تلاش لاگین بعدی مسدود خواهد شد یا نه:
1@Test
2public void givenLoginQueue_whenReachLimit_thenBlocked() {
3 int slots = 10;
4 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(slots);
5 LoginQueueUsingSemaphore loginQueue = new LoginQueueUsingSemaphore(slots);
6 IntStream.range(0, slots)
7 .forEach(user -> executorService.execute(loginQueue::tryLogin));
8 executorService.shutdown();
9
10 assertEquals(0, loginQueue.availableSlots());
11 assertFalse(loginQueue.tryLogin());
12}سپس بررسی میکنیم آیا هیچ اسلاتی پس از لاگآوت موجود است یا نه:
1@Test
2public void givenLoginQueue_whenLogout_thenSlotsAvailable() {
3 int slots = 10;
4 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(slots);
5 LoginQueueUsingSemaphore loginQueue = new LoginQueueUsingSemaphore(slots);
6 IntStream.range(0, slots)
7 .forEach(user -> executorService.execute(loginQueue::tryLogin));
8 executorService.shutdown();
9 assertEquals(0, loginQueue.availableSlots());
10 loginQueue.logout();
11
12 assertTrue(loginQueue.availableSlots() > 0);
13 assertTrue(loginQueue.tryLogin());
14}Semaphore زماندار
در این بخش به بررسی Apache Commons TimedSemaphore میپردازیم. TimedSemaphore به ما امکان میدهد که مانند Semaphore ساده چندین مجوز داشته باشیم، اما این مجوزها صرفاً در یک دوره زمانی مفروض موجود هستند و پس از طی شدن این دوره، زمان ریست میشود و همه مجوزها آزاد میشوند.
از TimedSemaphore میتوان برای ساختن یک صف با تأخیر مانند زیر استفاده کرد:
1class DelayQueueUsingTimedSemaphore {
2
3 private TimedSemaphore semaphore;
4
5 DelayQueueUsingTimedSemaphore(long period, int slotLimit) {
6 semaphore = new TimedSemaphore(period, TimeUnit.SECONDS, slotLimit);
7 }
8
9 boolean tryAdd() {
10 return semaphore.tryAcquire();
11 }
12
13 int availableSlots() {
14 return semaphore.getAvailablePermits();
15 }
16
17}زمانی که از یک صف با تأخیر که دارای دوره زمانی یک ثانیهای است، استفاده میکنیم، پس از مصرف همه اسلاتهای موجود درون آن یک ثانیه، نباید چیزی موجود باشد:
1public void givenDelayQueue_whenReachLimit_thenBlocked() {
2 int slots = 50;
3 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(slots);
4 DelayQueueUsingTimedSemaphore delayQueue
5 = new DelayQueueUsingTimedSemaphore(1, slots);
6
7 IntStream.range(0, slots)
8 .forEach(user -> executorService.execute(delayQueue::tryAdd));
9 executorService.shutdown();
10
11 assertEquals(0, delayQueue.availableSlots());
12 assertFalse(delayQueue.tryAdd());
13}اما پس از خوابیدن به مدت یک ثانیه، semaphore ریست شده و مجوزها را آزاد میکند:
1@Test
2public void givenDelayQueue_whenTimePass_thenSlotsAvailable() throws InterruptedException {
3 int slots = 50;
4 ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(slots);
5 DelayQueueUsingTimedSemaphore delayQueue = new DelayQueueUsingTimedSemaphore(1, slots);
6 IntStream.range(0, slots)
7 .forEach(user -> executorService.execute(delayQueue::tryAdd));
8 executorService.shutdown();
9
10 assertEquals(0, delayQueue.availableSlots());
11 Thread.sleep(1000);
12 assertTrue(delayQueue.availableSlots() > 0);
13 assertTrue(delayQueue.tryAdd());
14}Semaphore در برابر Mutex
Mutex مشابه یک semaphore دودویی عمل میکند، ما میتوانیم از آن برای پیادهسازی «انحصار متقابل» (Mutual Exclusion) استفاده کنیم. در مثال زیر، از یک semaphore ساده دودویی برای ساخت یک شمارنده استفاده کردهایم:
1class CounterUsingMutex {
2
3 private Semaphore mutex;
4 private int count;
5
6 CounterUsingMutex() {
7 mutex = new Semaphore(1);
8 count = 0;
9 }
10
11 void increase() throws InterruptedException {
12 mutex.acquire();
13 this.count = this.count + 1;
14 Thread.sleep(1000);
15 mutex.release();
16
17 }
18
19 int getCount() {
20 return this.count;
21 }
22
23 boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
24 return mutex.hasQueuedThreads();
25 }
26}زمانی که تعداد زیادی نخ به صورت یکباره برای دسترسی به یک شمارنده تلاش کنند، در یک صف مسدود میشوند:
1@Test
2public void whenMutexAndMultipleThreads_thenBlocked()
3 throws InterruptedException {
4 int count = 5;
5 ExecutorService executorService
6 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(count);
7 CounterUsingMutex counter = new CounterUsingMutex();
8 IntStream.range(0, count)
9 .forEach(user -> executorService.execute(() -> {
10 try {
11 counter.increase();
12 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
13 e.printStackTrace();
14 }
15 }));
16 executorService.shutdown();
17
18 assertTrue(counter.hasQueuedThreads());
19}زمانی که صبر کنیم، همه نخها به شمارنده دسترسی مییابند و هیچ نخی در صف باقی نمیماند:
1@Test
2public void givenMutexAndMultipleThreads_ThenDelay_thenCorrectCount()
3 throws InterruptedException {
4 int count = 5;
5 ExecutorService executorService
6 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(count);
7 CounterUsingMutex counter = new CounterUsingMutex();
8 IntStream.range(0, count)
9 .forEach(user -> executorService.execute(() -> {
10 try {
11 counter.increase();
12 } catch (InterruptedException e) {
13 e.printStackTrace();
14 }
15 }));
16 executorService.shutdown();
17
18 assertTrue(counter.hasQueuedThreads());
19 Thread.sleep(5000);
20 assertFalse(counter.hasQueuedThreads());
21 assertEquals(count, counter.getCount());
22}سخن پایانی
در این مقاله به بررسی مبانی مقدماتی semaphore در جاوا پرداختیم. کد همه موارد مطرحشده در این مقاله را میتوانید در این ریپوزیتوری گیتهاب (+) ببینید.
اگر این مطلب برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای جاوا
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- گنجینه آموزشهای جاوا (Java)
- آموزش جامع برنامه نویسی جاوا به زبان ساده — بخش هفتم: حالت تست
- زبان برنامه نویسی جاوا (Java) — از صفر تا صد
==