مساله تقسیم بندی در بهینه سازی — به زبان ساده
در این مطلب، روش حل مساله تقسیم بندی در بهینه سازی بیان شده است. همچنین، پیادهسازی روش آموزش داده شده در زبانهای برنامهنویسی گوناگون شامل «سیپلاسپلاس» (++C)، «سی» (C)، «جاوا» (Java)، «پایتون ۳» (Python 3) و «پیاچپی» (PHP) انجام شده است. «مساله تقسیم بندی» (Partition Problem) یکی از انواع مسائل بهینهسازی است. در مساله تقسیم بندی، هدف تقسیم کردن مساله به دو زیر مجموعه به گونهای است که مجموع مقادیر موجود در هر دو زیر مجموعه، با هم برابر باشد. مثال زیر در این راستا قابل توجه است:
arr[] = {1, 5, 11, 5}
Output: true
The array can be partitioned as {1, 5, 5} and {11}
arr[] = {1, 5, 3}
Output: false
The array cannot be partitioned into equal sum sets.
در ادامه، دو گام اساسی برای حل این مساله بیان شدهاند.
- مجموع آرایه را محاسبه کن. اگر مجموع عددی فرد باشد، دو زیر مجموعه با مجموع برابر وجود نخواهد داشت. بنابراین، مقدار False را بازگردان.
- اگر مجموع عناصر آرایه زوج است، مجموع تقسیم بر ۲ را محاسبه و سپس، زیرمجموعهای از آرایه با مجموع برابر با $$\frac{sum}{2}$$ را پیدا کن.
گام اول ساده و گام دوم مهم و حیاتی است. برای پیادهسازی گام دوم میتوان از راهکار بازگشتی یا برنامهنویسی پویا استفاده کرد.
راهکار بازگشتی برای حل مساله تقسیم بندی
در ادامه، راهکار بازگشتی برای پیادهسازی گام دوم بیان شده در بالا، ارائه شده است.
(isSubsetSum(arr, n, sum/2 تابعی است که اگر زیرمجموعهای از آرایه [arr[0..n-1 با مجموع برابر با $$\frac{Sum}{2}$$ وجود داشت، مقدار True را باز میگرداند.
مساله isSubsetSum را میتوان به دو زیر مسأله تقسیم کرد.
- ()isSubsetSum بدون در نظر گرفتن آخرین عنصر (کاهش n به n-1)
- isSubsetSum با در نظر گرفتن آخرین عنصر (کاهش $$\frac{Sum}{2}$$ با [arr[n-1 و n تا n-1)
اگر هر یک از دو زیرمسأله بالا مقدار true را بازگرداند، مقدار true را بازگردان.
isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum/2) = isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum/2) || isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum/2 - arr[n-1])
حل مساله تقسیم بندی به روش بازگشتی در ++C
1// A recursive C++ program for partition problem
2#include <bits/stdc++.h>
3using namespace std;
4
5// A utility function that returns true if there is
6// a subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
7bool isSubsetSum (int arr[], int n, int sum)
8{
9 // Base Cases
10 if (sum == 0)
11 return true;
12 if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
13 return false;
14
15 // If last element is greater than sum, then
16 // ignore it
17 if (arr[n-1] > sum)
18 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum);
19
20 /* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
21 the following
22 (a) including the last element
23 (b) excluding the last element
24 */
25 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum) ||
26 isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum-arr[n-1]);
27}
28
29// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
30// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
31bool findPartiion (int arr[], int n)
32{
33 // Calculate sum of the elements in array
34 int sum = 0;
35 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
36 sum += arr[i];
37
38 // If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
39 // with equal sum
40 if (sum%2 != 0)
41 return false;
42
43 // Find if there is subset with sum equal to
44 // half of total sum
45 return isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum/2);
46}
47
48// Driver program to test above function
49int main()
50{
51 int arr[] = {3, 1, 5, 9, 12};
52 int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
53 if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
54 cout << "Can be divided into two subsets "
55 "of equal sum";
56 else
57 cout << "Can not be divided into two subsets"
58 " of equal sum";
59 return 0;
60}
61
62// This code is contributed by rathbhupendraحل مساله تقسیم بندی به روش بازگشتی در C
1// A recursive C program for partition problem
2#include <stdio.h>
3#include <stdbool.h>
4
5// A utility function that returns true if there is
6// a subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
7bool isSubsetSum (int arr[], int n, int sum)
8{
9 // Base Cases
10 if (sum == 0)
11 return true;
12 if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
13 return false;
14
15 // If last element is greater than sum, then
16 // ignore it
17 if (arr[n-1] > sum)
18 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum);
19
20 /* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
21 the following
22 (a) including the last element
23 (b) excluding the last element
24 */
25 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum) ||
26 isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum-arr[n-1]);
27}
28
29// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
30// subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
31bool findPartiion (int arr[], int n)
32{
33 // Calculate sum of the elements in array
34 int sum = 0;
35 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
36 sum += arr[i];
37
38 // If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
39 // with equal sum
40 if (sum%2 != 0)
41 return false;
42
43 // Find if there is subset with sum equal to
44 // half of total sum
45 return isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum/2);
46}
47
48// Driver program to test above function
49int main()
50{
51 int arr[] = {3, 1, 5, 9, 12};
52 int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
53 if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
54 printf("Can be divided into two subsets "
55 "of equal sum");
56 else
57 printf("Can not be divided into two subsets"
58 " of equal sum");
59 return 0;
60}حل مساله تقسیم بندی به روش بازگشتی در جاوا
1// A recursive Java solution for partition problem
2import java.io.*;
3
4class Partition
5{
6 // A utility function that returns true if there is a
7 // subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
8 static boolean isSubsetSum (int arr[], int n, int sum)
9 {
10 // Base Cases
11 if (sum == 0)
12 return true;
13 if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
14 return false;
15
16 // If last element is greater than sum, then ignore it
17 if (arr[n-1] > sum)
18 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum);
19
20 /* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
21 the following
22 (a) including the last element
23 (b) excluding the last element
24 */
25 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum) ||
26 isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum-arr[n-1]);
27 }
28
29 // Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
30 // subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
31 static boolean findPartition (int arr[], int n)
32 {
33 // Calculate sum of the elements in array
34 int sum = 0;
35 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
36 sum += arr[i];
37
38 // If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
39 // with equal sum
40 if (sum%2 != 0)
41 return false;
42
43 // Find if there is subset with sum equal to half
44 // of total sum
45 return isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum/2);
46 }
47
48 /*Driver function to check for above function*/
49 public static void main (String[] args)
50 {
51
52 int arr[] = {3, 1, 5, 9, 12};
53 int n = arr.length;
54 if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
55 System.out.println("Can be divided into two "+
56 "subsets of equal sum");
57 else
58 System.out.println("Can not be divided into " +
59 "two subsets of equal sum");
60 }
61}
62/* This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal */حل مساله تقسیم بندی به روش بازگشتی در پایتون ۳
1# A recursive Python3 program for
2# partition problem
3
4# A utility function that returns
5# true if there is a subset of
6# arr[] with sun equal to given sum
7def isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum):
8 # Base Cases
9 if sum == 0:
10 return True
11 if n == 0 and sum != 0:
12 return False
13
14 # If last element is greater than sum, then
15 # ignore it
16 if arr[n-1] > sum:
17 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum)
18
19 ''' else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
20 the following
21 (a) including the last element
22 (b) excluding the last element'''
23
24 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum) or isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum-arr[n-1])
25
26# Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
27# subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
28def findPartion (arr, n):
29 # Calculate sum of the elements in array
30 sum = 0
31 for i in range(0, n):
32 sum += arr[i]
33 # If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
34 # with equal sum
35 if sum % 2 != 0:
36 return false
37
38 # Find if there is subset with sum equal to
39 # half of total sum
40 return isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum // 2)
41
42# Driver program to test above function
43arr = [3, 1, 5, 9, 12]
44n = len(arr)
45if findPartion(arr, n) == True:
46 print ("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
47else:
48 print ("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum")
49
50# This code is contributed by shreyanshi_arun.حل مساله تقسیم بندی به روش بازگشتی در #C
1// A recursive C# solution for partition problem
2using System;
3
4class GFG
5{
6 // A utility function that returns true if there is a
7 // subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
8 static bool isSubsetSum (int []arr, int n, int sum)
9 {
10 // Base Cases
11 if (sum == 0)
12 return true;
13 if (n == 0 && sum != 0)
14 return false;
15
16 // If last element is greater than sum, then ignore it
17 if (arr[n-1] > sum)
18 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum);
19
20 /* else, check if sum can be obtained by any of
21 the following
22 (a) including the last element
23 (b) excluding the last element
24 */
25 return isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum) ||
26 isSubsetSum (arr, n-1, sum-arr[n-1]);
27 }
28
29 // Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two
30 // subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
31 static bool findPartition (int []arr, int n)
32 {
33 // Calculate sum of the elements in array
34 int sum = 0;
35 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
36 sum += arr[i];
37
38 // If sum is odd, there cannot be two subsets
39 // with equal sum
40 if (sum%2 != 0)
41 return false;
42
43 // Find if there is subset with sum equal to half
44 // of total sum
45 return isSubsetSum (arr, n, sum/2);
46 }
47
48 // Driver function
49 public static void Main ()
50 {
51
52 int []arr = {3, 1, 5, 9, 12};
53 int n = arr.Length;
54 if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
55 Console.Write("Can be divided into two "+
56 "subsets of equal sum");
57 else
58 Console.Write("Can not be divided into " +
59 "two subsets of equal sum");
60 }
61}
62
63// This code is contributed by Sam007حل مساله تقسیم بندی به روش بازگشتی در PHP
1<?php
2// A recursive PHP solution for partition problem
3
4// A utility function that returns true if there is
5// a subset of arr[] with sun equal to given sum
6function isSubsetSum ($arr, $n, $sum)
7{
8 // Base Cases
9 if ($sum == 0)
10 return true;
11 if ($n == 0 && $sum != 0)
12 return false;
13
14 // If last element is greater than
15 // sum, then ignore it
16 if ($arr[$n - 1] > $sum)
17 return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1, $sum);
18
19 /* else, check if sum can be obtained
20 by any of the following
21 (a) including the last element
22 (b) excluding the last element
23 */
24 return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1, $sum) ||
25 isSubsetSum ($arr, $n - 1,
26 $sum - $arr[$n - 1]);
27}
28
29// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
30// in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise false
31function findPartiion ($arr, $n)
32{
33 // Calculate sum of the elements
34 // in array
35 $sum = 0;
36 for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
37 $sum += $arr[$i];
38
39 // If sum is odd, there cannot be
40 // two subsets with equal sum
41 if ($sum % 2 != 0)
42 return false;
43
44 // Find if there is subset with sum
45 // equal to half of total sum
46 return isSubsetSum ($arr, $n, $sum / 2);
47}
48
49// Driver Code
50$arr = array(3, 1, 5, 9, 12);
51$n = count($arr);
52if (findPartiion($arr, $n) == true)
53 echo "Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum";
54else
55 echo "Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum";
56
57// This code is contributed by rathbhupendra
58?>خروجی قطعه کدهای بالا به صورت زیر است.
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
پیچیدگی زمانی این روش در بدترین حالت از درجه (O(2n است. این روش دو احتمال (در نظر گرفتن یا نگرفتن) را برای هر یک از عناصر میسنجد.
راهکار برنامه نویسی پویا برای حل مساله تقسیم بندی
این مساله را میتوان هنگامی که مجموع عناصر خیلی بزرگ نیست، با استفاده از «برنامهنویسی پویا» (Dynamic Programming) نیز حل کرد. میتوان یک آرایه دوبُعدی [][]part با اندازه $$(\frac{sum}{2})*(n+1)$$ ساخت.
همچنین، میتوان راهکار را به صورت پایین به بالا به گونهای ساخت که هر ورودی دارای خصوصیات زیر باشد.
part[i][j] = true if a subset of {arr[0], arr[1], ..arr[j-1]} has sum
equal to i, otherwise false
حل مساله تقسیم بندی با برنامهنویسی پویا در ++C/C
1// A Dynamic Programming based C program to partition problem
2#include <stdio.h>
3
4// Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two subsets of
5// equal sum, otherwise false
6bool findPartiion (int arr[], int n)
7{
8 int sum = 0;
9 int i, j;
10
11 // Caculcate sun of all elements
12 for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
13 sum += arr[i];
14
15 if (sum%2 != 0)
16 return false;
17
18 bool part[sum/2+1][n+1];
19
20 // initialize top row as true
21 for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
22 part[0][i] = true;
23
24 // initialize leftmost column, except part[0][0], as 0
25 for (i = 1; i <= sum/2; i++)
26 part[i][0] = false;
27
28 // Fill the partition table in botton up manner
29 for (i = 1; i <= sum/2; i++)
30 {
31 for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
32 {
33 part[i][j] = part[i][j-1];
34 if (i >= arr[j-1])
35 part[i][j] = part[i][j] || part[i - arr[j-1]][j-1];
36 }
37 }
38
39 /* // uncomment this part to print table
40 for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
41 {
42 for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
43 printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
44 printf("\n");
45 } */
46
47 return part[sum/2][n];
48}
49
50// Driver program to test above funtion
51int main()
52{
53 int arr[] = {3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1};
54 int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
55 if (findPartiion(arr, n) == true)
56 printf("Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
57 else
58 printf("Can not be divided into two subsets of equal sum");
59 getchar();
60 return 0;
61}حل مساله تقسیم بندی با برنامهنویسی پویا در جاوا
1// A dynamic programming based Java program for partition problem
2import java.io.*;
3
4class Partition {
5
6 // Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned in two subsets of
7 // equal sum, otherwise false
8 static boolean findPartition (int arr[], int n)
9 {
10 int sum = 0;
11 int i, j;
12
13 // Caculcate sun of all elements
14 for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
15 sum += arr[i];
16
17 if (sum%2 != 0)
18 return false;
19
20 boolean part[][]=new boolean[sum/2+1][n+1];
21
22 // initialize top row as true
23 for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
24 part[0][i] = true;
25
26 // initialize leftmost column, except part[0][0], as 0
27 for (i = 1; i <= sum/2; i++)
28 part[i][0] = false;
29
30 // Fill the partition table in botton up manner
31 for (i = 1; i <= sum/2; i++)
32 {
33 for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
34 {
35 part[i][j] = part[i][j-1];
36 if (i >= arr[j-1])
37 part[i][j] = part[i][j] ||
38 part[i - arr[j-1]][j-1];
39 }
40 }
41
42 /* // uncomment this part to print table
43 for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
44 {
45 for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
46 printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
47 printf("\n");
48 } */
49
50 return part[sum/2][n];
51 }
52
53 /*Driver function to check for above function*/
54 public static void main (String[] args)
55 {
56 int arr[] = {3, 1, 1, 2, 2,1};
57 int n = arr.length;
58 if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
59 System.out.println("Can be divided into two "
60 "subsets of equal sum");
61 else
62 System.out.println("Can not be divided into"
63 " two subsets of equal sum");
64
65 }
66}
67/* This code is contributed by Devesh Agrawal */حل مساله تقسیم بندی با برنامهنویسی پویا در پایتون ۳
1# Dynamic Programming based python
2# program to partition problem
3
4# Returns true if arr[] can be
5# partitioned in two subsets of
6# equal sum, otherwise false
7def findPartition(arr, n):
8 sum = 0
9 i, j = 0, 0
10
11 # calculate sum of all elements
12 for i in range(n):
13 sum += arr[i]
14
15 if sum % 2 != 0:
16 return false
17
18 part = [[ True for i in range(n + 1)]
19 for j in range(sum // 2 + 1)]
20
21 # initialize top row as true
22 for i in range(0, n + 1):
23 part[0][i] = True
24
25 # intialize leftmost column,
26 # except part[0][0], as 0
27 for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
28 part[i][0] = False
29
30 # fill the partition table in
31 # bottom up manner
32 for i in range(1, sum // 2 + 1):
33
34 for j in range(1, n + 1):
35 part[i][j] = part[i][j - 1]
36
37 if i >= arr[j - 1]:
38 part[i][j] = (part[i][j] or
39 part[i - arr[j - 1]][j - 1])
40
41 return part[sum // 2][n]
42
43# Driver Code
44arr = [3, 1, 1, 2, 2, 1]
45n = len(arr)
46if findPartition(arr, n) == True:
47 print("Can be divided into two",
48 "subsets of equal sum")
49else:
50 print("Can not be divided into ",
51 "two subsets of equal sum")
52
53# This code is contributed
54# by mohit kumar 29 حل مساله تقسیم بندی با برنامهنویسی پویا در #C
1// A dynamic programming based C# program
2// for partition problem
3using System;
4
5class GFG {
6
7 // Returns true if arr[] can be partitioned
8 // in two subsets of equal sum, otherwise
9 // false
10 static bool findPartition (int []arr, int n)
11 {
12
13 int sum = 0;
14 int i, j;
15
16 // Caculcate sun of all elements
17 for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
18 sum += arr[i];
19
20 if (sum % 2 != 0)
21 return false;
22
23 bool [, ]part=new bool[sum / 2 + 1, n + 1];
24
25 // initialize top row as true
26 for (i = 0; i <= n; i++)
27 part[0, i] = true;
28
29 // initialize leftmost column, except
30 // part[0][0], as 0
31 for (i = 1; i <= sum/2; i++)
32 part[i, 0] = false;
33
34 // Fill the partition table in botton
35 // up manner
36 for (i = 1; i <= sum/2; i++)
37 {
38 for (j = 1; j <= n; j++)
39 {
40 part[i, j] = part[i, j - 1];
41 if (i >= arr[j - 1])
42 part[i, j] = part[i, j] ||
43 part[i - arr[j - 1],j - 1];
44 }
45 }
46
47 /* // uncomment this part to print table
48 for (i = 0; i <= sum/2; i++)
49 {
50 for (j = 0; j <= n; j++)
51 printf ("%4d", part[i][j]);
52 printf("\n");
53 } */
54
55 return part[sum / 2, n];
56 }
57
58 // Driver program to test above funtion
59 public static void Main ()
60 {
61 int []arr = {3, 1, 1, 2, 2,1};
62 int n = arr.Length;
63
64 if (findPartition(arr, n) == true)
65 Console.Write("Can be divided"
66 + " into two subsets of"
67 + " equal sum");
68 else
69 Console.Write("Can not be "
70 + "divided into two subsets"
71 + " of equal sum");
72
73 }
74}
75
76// This code is contributed by Sam007.خروجی قطعه کدهای بالا به صورت زیر است.
Can be divided into two subsets of equal sum
نمودار زیر، مقادیر را در جدول تقسیمبندی نشان میدهد.
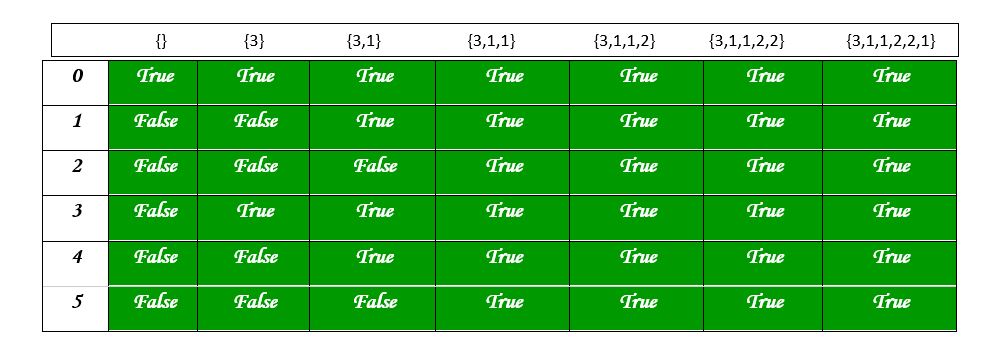
پیچیدگی زمانی این روش از درجه (O(sum*n و فضای کمکی آن از درجه (O(sum*n است. شایان توجه است که این روش برای آرایههایی با مجموع بزرگ قابل استفاده نیست.
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- آموزش برنامهنویسی C++
- مجموعه آموزشهای ریاضیات
- یافتن دور همیلتونی با الگوریتم پس گرد — به زبان ساده
- الگوریتم بازی مار و پله همراه با کد — به زبان ساده
- حل مساله n وزیر با الگوریتم پسگرد (Backtracking) — به زبان ساده
- الگوریتم جست و جوی دودویی در جاوا اسکریپت — به زبان ساده
^^