مرتب سازی هرمی تکرار شونده — به زبان ساده
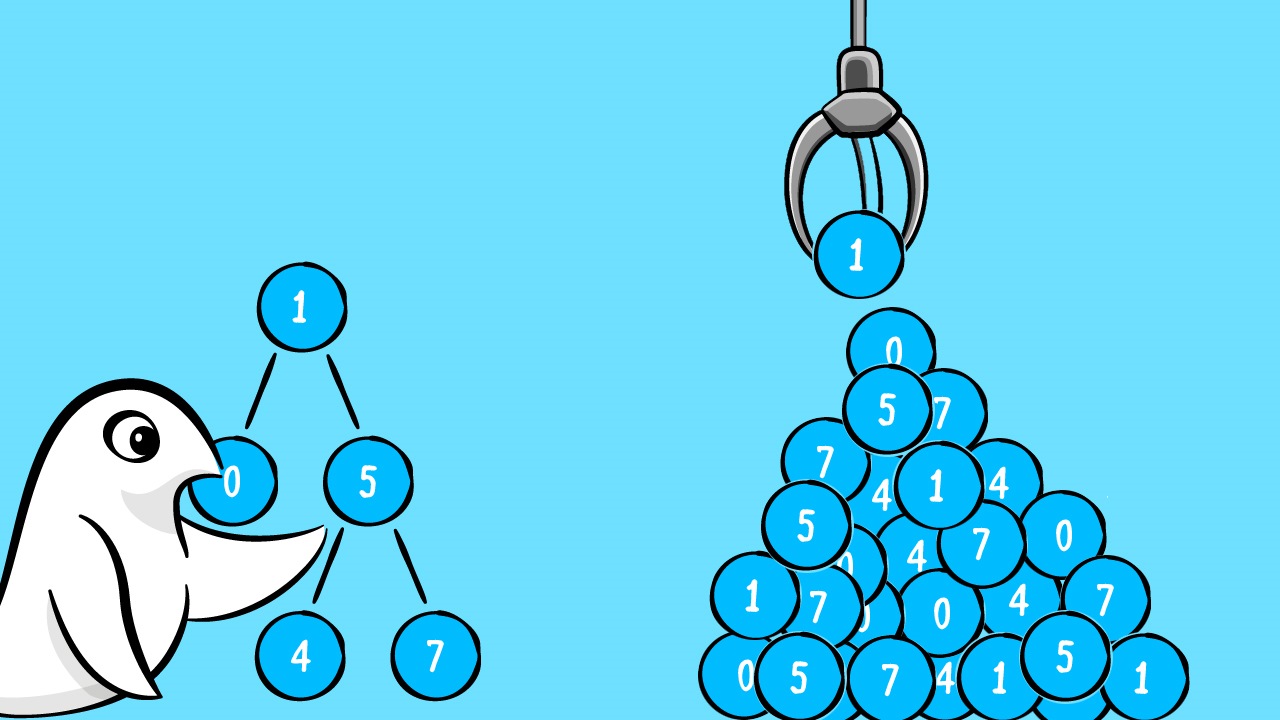
در این مطلب، به «مرتب سازی هرمی تکرار شونده» (Iterative HeapSort) پرداختهایم که در واقع همان الگوریتم مرتب سازی هرمی است که به روش تکرار شونده (Iterative) پیادهسازی شده است. همچنین، پیادهسازی الگوریتم مرتب سازی هرمی تکرار شونده در زبانهای برنامهنویسی «سیپلاسپلاس» (++C)، «جاوا» (Java) و «پایتون» (Python) پیادهسازی شده است. «مرتبسازی هرمی» (HeapSort) گونهای از الگوریتمهای مبتنی بر مقایسه است که طی آن، ابتدا درخت بیشینه ساخته میشود و سپس عنصر ریشه با آخرین عنصر (به تعداد اندازه) جایگزین میشود و مشخصات هرم را هر بار نگهداری میکند تا در نهایت آن را مرتب کند. مثال زیر برای درک بهتر این مفهوم بیان شده است.
Input : 10 20 15 17 9 21 Output : 9 10 15 17 20 21 Input: 12 11 13 5 6 7 15 5 19 Output: 5 5 6 7 11 12 13 15 19
در مثال اول، ابتدا باید هرم بیشینه ساخته شود. بنابراین، کار با عدد ۲۰ به عنوان فرزند آغاز میشود و والدین آن بررسی میشوند. در اینجا، ۱۰ کوچکتر است. بنابراین این دو با یکدیگر جا به جا میشوند. داریم: $$20\; 10\; 15\; 17\; 9\; 21$$. اکنون، فرزند ۱۷ بزرگتر از والد خودش یعنی ۱۰ است. بنابراین، هر دو با هم جا به جا میشوند و ترتیب آنها $$20\; 17\; 15\; 10\; 9\; 21$$ خواهد بود. اکنون، فرزند ۲۱ بزرگتر از والد خود یعنی ۱۵ است. بنابراین، هر دو با یکدیگر جایگزین میشوند.
داریم: $$20\; 17\; 21\; 10\; 9\; 15$$. اکنون، ۲۱ بزرگتر از والد خودش ۲۰ است. بنابراین: $$21\; 17\; 20\; 10\; 9\; 15$$. این «هرم بیشینه» (Max Heap) است. اکنون باید مرتبسازی اعمال شود. در اینجا باید اولین عنصر با آخرین عنصر جا به جا شود و در عین حال، خصوصیات هرم بیشینه نیز حفظ شود. بنابراین، بعد از اولین جا به جایی $$15\; 17\; 20\; 10\; 9\; 21$$ را داریم که این مورد، نقض خصوصیات هرم بیشینه است؛ بنابراین، باید آن را حفظ کرد. در نهایت، ترتیب به صورت زیر خواهد بود.
20 17 15 10 9 21
17 10 15 9 20 21
15 10 9 17 20 21
10 9 15 17 20 21
9 10 15 17 20 21
در اینجا، قسمت زیر خطدار، در واقع همان قسمت مرتب شده است.
مرتب سازی هرمی تکرار شونده در ++C
1// C++ program for implementation
2// of Iterative Heap Sort
3#include <bits/stdc++.h>
4using namespace std;
5
6// function build Max Heap where value
7// of each child is always smaller
8// than value of their parent
9void buildMaxHeap(int arr[], int n)
10{
11 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
12 {
13 // if child is bigger than parent
14 if (arr[i] > arr[(i - 1) / 2])
15 {
16 int j = i;
17
18 // swap child and parent until
19 // parent is smaller
20 while (arr[j] > arr[(j - 1) / 2])
21 {
22 swap(arr[j], arr[(j - 1) / 2]);
23 j = (j - 1) / 2;
24 }
25 }
26 }
27}
28
29void heapSort(int arr[], int n)
30{
31 buildMaxHeap(arr, n);
32
33 for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
34 {
35 // swap value of first indexed
36 // with last indexed
37 swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
38
39 // maintaining heap property
40 // after each swapping
41 int j = 0, index;
42
43 do
44 {
45 index = (2 * j + 1);
46
47 // if left child is smaller than
48 // right child point index variable
49 // to right child
50 if (arr[index] < arr[index + 1] &&
51 index < (i - 1))
52 index++;
53
54 // if parent is smaller than child
55 // then swapping parent with child
56 // having higher value
57 if (arr[j] < arr[index] && index < i)
58 swap(arr[j], arr[index]);
59
60 j = index;
61
62 } while (index < i);
63 }
64}
65
66// Driver Code to test above
67int main()
68{
69 int arr[] = {10, 20, 15, 17, 9, 21};
70 int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
71
72 printf("Given array: ");
73 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
74 printf("%d ", arr[i]);
75
76 printf("\n\n");
77
78 heapSort(arr, n);
79
80 // print array after sorting
81 printf("Sorted array: ");
82 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
83 printf("%d ", arr[i]);
84
85 return 0;
86} مرتب سازی هرمی تکرار شونده در جاوا
1// Java implementation of Iterative Heap Sort
2public class HeapSort {
3
4 // function build Max Heap where value
5 // of each child is always smaller
6 // than value of their parent
7 static void buildMaxHeap(int arr[], int n)
8 {
9 for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
10 {
11 // if child is bigger than parent
12 if (arr[i] > arr[(i - 1) / 2])
13 {
14 int j = i;
15
16 // swap child and parent until
17 // parent is smaller
18 while (arr[j] > arr[(j - 1) / 2])
19 {
20 swap(arr, j, (j - 1) / 2);
21 j = (j - 1) / 2;
22 }
23 }
24 }
25 }
26
27 static void heapSort(int arr[], int n)
28 {
29 buildMaxHeap(arr, n);
30
31 for (int i = n - 1; i > 0; i--)
32 {
33 // swap value of first indexed
34 // with last indexed
35 swap(arr, 0, i);
36
37 // maintaining heap property
38 // after each swapping
39 int j = 0, index;
40
41 do
42 {
43 index = (2 * j + 1);
44
45 // if left child is smaller than
46 // right child point index variable
47 // to right child
48 if (index < (i - 1) && arr[index] < arr[index + 1])
49 index++;
50
51 // if parent is smaller than child
52 // then swapping parent with child
53 // having higher value
54 if (index < i && arr[j] < arr[index])
55 swap(arr, j, index);
56
57 j = index;
58
59 } while (index < i);
60 }
61 }
62
63 public static void swap(int[] a, int i, int j) {
64 int temp = a[i];
65 a[i]=a[j];
66 a[j] = temp;
67 }
68
69 /* A utility function to print array of size n */
70 static void printArray(int arr[])
71 {
72 int n = arr.length;
73 for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
74 System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
75 System.out.println();
76 }
77
78 // Driver program
79 public static void main(String args[])
80 {
81 int arr[] = {10, 20, 15, 17, 9, 21};
82 int n = arr.length;
83
84 System.out.print("Given array: ");
85 printArray(arr);
86
87 heapSort(arr, n);
88
89 System.out.print("Sorted array: ");
90 printArray(arr);
91 }
92}مرتب سازی هرمی تکرار شونده در پایتون ۳
1# Python3 program for implementation
2# of Iterative Heap Sort
3
4# function build Max Heap where value
5# of each child is always smaller
6# than value of their parent
7def buildMaxHeap(arr, n):
8
9 for i in range(n):
10
11 # if child is bigger than parent
12 if arr[i] > arr[int((i - 1) / 2)]:
13 j = i
14
15 # swap child and parent until
16 # parent is smaller
17 while arr[j] > arr[int((j - 1) / 2)]:
18 (arr[j],
19 arr[int((j - 1) / 2)]) = (arr[int((j - 1) / 2)],
20 arr[j])
21 j = int((j - 1) / 2)
22
23def heapSort(arr, n):
24
25 buildMaxHeap(arr, n)
26
27 for i in range(n - 1, 0, -1):
28
29 # swap value of first indexed
30 # with last indexed
31 arr[0], arr[i] = arr[i], arr[0]
32
33 # maintaining heap property
34 # after each swapping
35 j, index = 0, 0
36
37 while True:
38 index = 2 * j + 1
39
40 # if left child is smaller than
41 # right child point index variable
42 # to right child
43 if (index < (i - 1) and
44 arr[index] < arr[index + 1]):
45 index += 1
46
47 # if parent is smaller than child
48 # then swapping parent with child
49 # having higher value
50 if index < i and arr[j] < arr[index]:
51 arr[j], arr[index] = arr[index], arr[j]
52
53 j = index
54 if index >= i:
55 break
56
57# Driver Code
58if __name__ == '__main__':
59 arr = [10, 20, 15, 17, 9, 21]
60 n = len(arr)
61
62 print("Given array: ")
63 for i in range(n):
64 print(arr[i], end = " ")
65
66 print()
67
68 heapSort(arr, n)
69
70 # print array after sorting
71 print("Sorted array: ")
72 for i in range(n):
73 print(arr[i], end = " ")
74
75# This code is contributed by PranchalKخروجی قطعه کدهای بالا، به صورت زیر است.
Given array: 10 20 15 17 9 21 Sorted array: 9 10 15 17 20 21
در اینجا، هر دو تابع buildMaxHeap و heapSort از درجه O(nlogn) هستند.
بنابراین، پیچیدگی زمانی کلی برابر با (O(nlogn است.
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای ساختمان داده و طراحی الگوریتم
- آموزش ساختمان دادهها با C و ++C (همراه با حل نمونه سوالات کنکور ارشد)
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- مرتبسازی پشته با الگوریتم بازگشتی — به زبان ساده
- مرتبسازی درجی (Insertion Sort) — به زبان ساده
- مرتبسازی حبابی و پیاده سازی آن — از صفر تا صد
^^