مرتب سازی درجی (Insertion Sort) — به زبان ساده
«مرتب سازی درجی» (Insertion Sort) یک الگوریتم مرتبسازی ساده است که روش عملکرد آن مشابه روشی است که افراد کارتهای بازی را در دست خود مرتب میکنند. در این مطلب، به الگوریتم مرتب سازی درجی پرداخته شده و سپس، پیادهسازی آن در زبانهای برنامهنویسی گوناگون، شامل «سیپلاسپلاس» (++C ،(C، «جاوا» (Java)، «پایتون» (Python)، «سیشارپ» (#C) و «پیاچپی» (PHP) انجام شده است.
الگوریتم مرتب سازی درجی
//مرتبسازی آرایه []arr با سایز n
- (insertionSort(arr, n
- از i = 1 تا n-1 حلقه بزن
- عنصر [arr[i را انتخاب کن و آن را در توالی مرتب شده [arr[0…i-1 درج کن
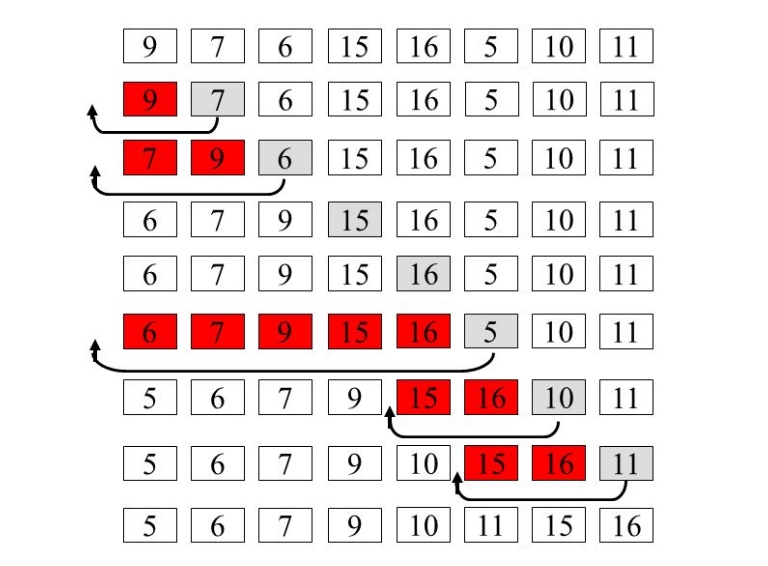
مثال اول از مرتب سازی درجی
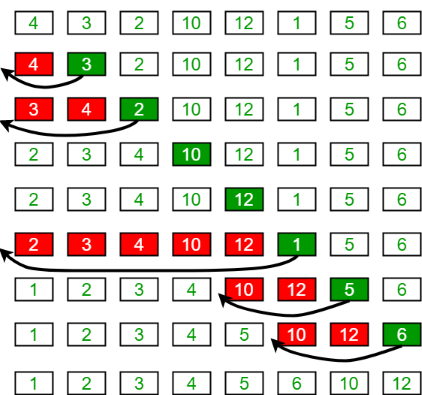
مثال دوم از مرتب سازی درجی
12, 11, 13, 5, 6
از i = 1 (دومین عنصر از آرایه) تا ۴ (آخرین عنصر از آرایه) حلقه بزن.
i = 1. به دلیل آنکه ۱۱ از ۱۲ کوچکتر است، ۱۲ را جا به جا کن و ۱۱ را پیش از ۱۲ درج کن.
i = 2. عدد ۱۳ در جای خود باقی میماند، زیرا همه عناصر [A[0..I-1 کوچکتر از ۱۳ هستند.
11, 12, 13, 5, 6
i = 3. عدد ۵ به آغاز منتقل میشود و همه عناصر دیگر، از ۱۱ تا ۱۳ یک خانه از خانه کنونی خود رو به جلو، جا به جا میشوند.
5, 11, 12, 13, 6
i = 4. عدد ۶ به خانه پس از ۵ منتقل میشود و عناصر از ۱۱ تا ۱۳ به اندازه یک خانه از خانه کنونیشان، به جلو میروند.
5, 6, 11, 12, 13
کد مرتب سازی درجی در ++C
1// C++ program for insertion sort
2#include <bits/stdc++.h>
3using namespace std;
4
5/* Function to sort an array using insertion sort*/
6void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
7{
8 int i, key, j;
9 for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
10 {
11 key = arr[i];
12 j = i - 1;
13
14 /* Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are
15 greater than key, to one position ahead
16 of their current position */
17 while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key)
18 {
19 arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
20 j = j - 1;
21 }
22 arr[j + 1] = key;
23 }
24}
25
26// A utility function to print an array of size n
27void printArray(int arr[], int n)
28{
29 int i;
30 for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
31 cout << arr[i] << " ";
32 cout << endl;
33}
34
35/* Driver code */
36int main()
37{
38 int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
39 int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
40
41 insertionSort(arr, n);
42 printArray(arr, n);
43
44 return 0;
45}
46
47// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendraکد مرتب سازی درجی در C
1// C program for insertion sort
2#include <math.h>
3#include <stdio.h>
4
5/* Function to sort an array using insertion sort*/
6void insertionSort(int arr[], int n)
7{
8 int i, key, j;
9 for (i = 1; i < n; i++) {
10 key = arr[i];
11 j = i - 1;
12
13 /* Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are
14 greater than key, to one position ahead
15 of their current position */
16 while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
17 arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
18 j = j - 1;
19 }
20 arr[j + 1] = key;
21 }
22}
23
24// A utility function to print an array of size n
25void printArray(int arr[], int n)
26{
27 int i;
28 for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
29 printf("%d ", arr[i]);
30 printf("\n");
31}
32
33/* Driver program to test insertion sort */
34int main()
35{
36 int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
37 int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
38
39 insertionSort(arr, n);
40 printArray(arr, n);
41
42 return 0;
43}کد مرتب سازی درجی در جاوا
1// Java program for implementation of Insertion Sort
2class InsertionSort {
3 /*Function to sort array using insertion sort*/
4 void sort(int arr[])
5 {
6 int n = arr.length;
7 for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
8 int key = arr[i];
9 int j = i - 1;
10
11 /* Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are
12 greater than key, to one position ahead
13 of their current position */
14 while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
15 arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
16 j = j - 1;
17 }
18 arr[j + 1] = key;
19 }
20 }
21
22 /* A utility function to print array of size n*/
23 static void printArray(int arr[])
24 {
25 int n = arr.length;
26 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
27 System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
28
29 System.out.println();
30 }
31
32 // Driver method
33 public static void main(String args[])
34 {
35 int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
36
37 InsertionSort ob = new InsertionSort();
38 ob.sort(arr);
39
40 printArray(arr);
41 }
42} /* This code is contributed by Rajat Mishra. */کد مرتب سازی درجی در پایتون
1# Python program for implementation of Insertion Sort
2
3# Function to do insertion sort
4def insertionSort(arr):
5
6 # Traverse through 1 to len(arr)
7 for i in range(1, len(arr)):
8
9 key = arr[i]
10
11 # Move elements of arr[0..i-1], that are
12 # greater than key, to one position ahead
13 # of their current position
14 j = i-1
15 while j >= 0 and key < arr[j] :
16 arr[j + 1] = arr[j]
17 j -= 1
18 arr[j + 1] = key
19
20
21# Driver code to test above
22arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6]
23insertionSort(arr)
24for i in range(len(arr)):
25 print ("% d" % arr[i])
26
27# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumraکد مرتب سازی درجی در #C
1// C# program for implementation of Insertion Sort
2using System;
3
4class InsertionSort {
5
6 // Function to sort array
7 // using insertion sort
8 void sort(int[] arr)
9 {
10 int n = arr.Length;
11 for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
12 int key = arr[i];
13 int j = i - 1;
14
15 // Move elements of arr[0..i-1],
16 // that are greater than key,
17 // to one position ahead of
18 // their current position
19 while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
20 arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
21 j = j - 1;
22 }
23 arr[j + 1] = key;
24 }
25 }
26
27 // A utility function to print
28 // array of size n
29 static void printArray(int[] arr)
30 {
31 int n = arr.Length;
32 for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
33 Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
34
35 Console.Write("\n");
36 }
37
38 // Driver Code
39 public static void Main()
40 {
41 int[] arr = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6 };
42 InsertionSort ob = new InsertionSort();
43 ob.sort(arr);
44 printArray(arr);
45 }
46}
47
48// This code is contributed by ChitraNayal.کد مرتب سازی درجی در PHP
1<?php
2// PHP program for insertion sort
3
4// Function to sort an array
5// using insertion sort
6function insertionSort(&$arr, $n)
7{
8 for ($i = 1; $i < $n; $i++)
9 {
10 $key = $arr[$i];
11 $j = $i-1;
12
13 // Move elements of arr[0..i-1],
14 // that are greater than key, to
15 // one position ahead of their
16 // current position
17 while ($j >= 0 && $arr[$j] > $key)
18 {
19 $arr[$j + 1] = $arr[$j];
20 $j = $j - 1;
21 }
22
23 $arr[$j + 1] = $key;
24 }
25}
26
27// A utility function to
28// print an array of size n
29function printArray(&$arr, $n)
30{
31 for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
32 echo $arr[$i]." ";
33 echo "\n";
34}
35
36// Driver Code
37$arr = array(12, 11, 13, 5, 6);
38$n = sizeof($arr);
39insertionSort($arr, $n);
40printArray($arr, $n);
41
42// This code is contributed by ChitraNayal.
43?>خروجی
خروجی قطعه کدهای بالا، برای آرایه [6, 5, 13, 11, 12] به صورت زیر است.
5 6 11 12 13
پیچیدگی زمانی: (O(n*2
فضای کمکی: (O(1
موارد مرزی (Boundary Cases): مرتب سازی درجی، در صورتی که عناصر دارای ترتیب برعکس باشند، بیشترین زمان اجرا را میبرد. همچنین، در صورتی که عناصر مرتب شده باشند، کمترین زمان اجرا (از درجه n) را خواهد داشت.
مرتبسازی درجا: بله
پایدار: بله
آنلاین: بله
کاربردها: مرتبسازی درجی، هنگامی مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد که تعداد عناصر کم باشد. همچنین، هنگامی که آرایه ورودی تقریبا مرتب شده باشد و تنها چند عنصر در یک آرایه بزرگ در جای نادرست قرار داشته باشند، مرتب سازی درجی گزینه مناسبی خواهد بود.
مرتب سازی درجی دودویی
هنگامی که از جستجوی دودویی برای کاهش تعداد مقایسهها در مرتب سازی درجی استفاده میشود، به آن مرتب سازی درجی دودویی گفته میشود. مرتب سازی درجی دودویی از جستجوی دودویی به منظور پیدا کردن موقعیت مناسب برای درج عناصر انتخاب شده در هر تکرار استفاده میشود.
در درج نرمال، مرتبسازی در بدترین حالت (O(i به طور میانجامد (در iاُمین تکرار). این مقدار را میتوان با استفاده از جستجوی دودویی به (O(logi کاهش داد. به طور کلی، الگوریتم همچنان دارای زمان اجرای (O(n2 است، زیرا مجموعهای از جا به جاییها برای هر درج مورد نیاز است.
پیادهسازی مرتب سازی درجی برای لیستهای پیوندی
در ادامه، پیادهسازی سادهای از مرتب سازی درجی برای لیستهای پیوندی ارائه شده است.
- یک لیست خالی «مرتب شده» (Sorted) (یا «نتیجه» (Result)) بساز.
- لیست داده شده را معکوس کن و اقدامات زیر را برای هر گره انجام بده:
- گره کنونی را به صورت مرتب شده، در لیست «مرتب شده» (Sorted) یا «نتیجه» (Result) قرار بده.
- سر لیست پیوندی داده شده را به سر لیست مرتب شده (یا نتیجه) تغییر بده.
کد مرتب سازی درجی در لیستهای پیوندی در ++C
1/* C program for insertion sort on a linked list */
2#include<stdio.h>
3#include<stdlib.h>
4
5/* Link list node */
6struct Node
7{
8 int data;
9 struct Node* next;
10};
11
12// Function to insert a given node in a sorted linked list
13void sortedInsert(struct Node**, struct Node*);
14
15// function to sort a singly linked list using insertion sort
16void insertionSort(struct Node **head_ref)
17{
18 // Initialize sorted linked list
19 struct Node *sorted = NULL;
20
21 // Traverse the given linked list and insert every
22 // node to sorted
23 struct Node *current = *head_ref;
24 while (current != NULL)
25 {
26 // Store next for next iteration
27 struct Node *next = current->next;
28
29 // insert current in sorted linked list
30 sortedInsert(&sorted, current);
31
32 // Update current
33 current = next;
34 }
35
36 // Update head_ref to point to sorted linked list
37 *head_ref = sorted;
38}
39
40/* function to insert a new_node in a list. Note that this
41 function expects a pointer to head_ref as this can modify the
42 head of the input linked list (similar to push())*/
43void sortedInsert(struct Node** head_ref, struct Node* new_node)
44{
45 struct Node* current;
46 /* Special case for the head end */
47 if (*head_ref == NULL || (*head_ref)->data >= new_node->data)
48 {
49 new_node->next = *head_ref;
50 *head_ref = new_node;
51 }
52 else
53 {
54 /* Locate the node before the point of insertion */
55 current = *head_ref;
56 while (current->next!=NULL &&
57 current->next->data < new_node->data)
58 {
59 current = current->next;
60 }
61 new_node->next = current->next;
62 current->next = new_node;
63 }
64}
65
66/* BELOW FUNCTIONS ARE JUST UTILITY TO TEST sortedInsert */
67
68/* Function to print linked list */
69void printList(struct Node *head)
70{
71 struct Node *temp = head;
72 while(temp != NULL)
73 {
74 printf("%d ", temp->data);
75 temp = temp->next;
76 }
77}
78
79/* A utility function to insert a node at the beginning of linked list */
80void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
81{
82 /* allocate node */
83 struct Node* new_node = new Node;
84
85 /* put in the data */
86 new_node->data = new_data;
87
88 /* link the old list off the new node */
89 new_node->next = (*head_ref);
90
91 /* move the head to point to the new node */
92 (*head_ref) = new_node;
93}
94
95
96// Driver program to test above functions
97int main()
98{
99 struct Node *a = NULL;
100 push(&a, 5);
101 push(&a, 20);
102 push(&a, 4);
103 push(&a, 3);
104 push(&a, 30);
105
106 printf("Linked List before sorting \n");
107 printList(a);
108
109 insertionSort(&a);
110
111 printf("\nLinked List after sorting \n");
112 printList(a);
113
114 return 0;
115} کد مرتب سازی درجی در لیستهای پیوندی در جاوا
1// Java program to sort link list
2// using insertion sort
3
4public class LinkedlistIS
5{
6 node head;
7 node sorted;
8
9 class node
10 {
11 int val;
12 node next;
13
14 public node(int val)
15 {
16 this.val = val;
17 }
18 }
19
20 void push(int val)
21 {
22 /* allocate node */
23 node newnode = new node(val);
24 /* link the old list off the new node */
25 newnode.next = head;
26 /* move the head to point to the new node */
27 head = newnode;
28 }
29
30 // function to sort a singly linked list using insertion sort
31 void insertionSort(node headref)
32 {
33 // Initialize sorted linked list
34 sorted = null;
35 node current = headref;
36 // Traverse the given linked list and insert every
37 // node to sorted
38 while (current != null)
39 {
40 // Store next for next iteration
41 node next = current.next;
42 // insert current in sorted linked list
43 sortedInsert(current);
44 // Update current
45 current = next;
46 }
47 // Update head_ref to point to sorted linked list
48 head = sorted;
49 }
50
51 /*
52 * function to insert a new_node in a list. Note that
53 * this function expects a pointer to head_ref as this
54 * can modify the head of the input linked list
55 * (similar to push())
56 */
57 void sortedInsert(node newnode)
58 {
59 /* Special case for the head end */
60 if (sorted == null || sorted.val >= newnode.val)
61 {
62 newnode.next = sorted;
63 sorted = newnode;
64 }
65 else
66 {
67 node current = sorted;
68 /* Locate the node before the point of insertion */
69 while (current.next != null && current.next.val < newnode.val)
70 {
71 current = current.next;
72 }
73 newnode.next = current.next;
74 current.next = newnode;
75 }
76 }
77
78 /* Function to print linked list */
79 void printlist(node head)
80 {
81 while (head != null)
82 {
83 System.out.print(head.val + " ");
84 head = head.next;
85 }
86 }
87
88 // Driver program to test above functions
89 public static void main(String[] args)
90 {
91 LinkedlistIS list = new LinkedlistIS();
92 list.push(5);
93 list.push(20);
94 list.push(4);
95 list.push(3);
96 list.push(30);
97 System.out.println("Linked List before Sorting..");
98 list.printlist(list.head);
99 list.insertionSort(list.head);
100 System.out.println("\nLinkedList After sorting");
101 list.printlist(list.head);
102 }
103}
104
105// This code is contributed by Rishabh Mahrseeکد مرتب سازی درجی در لیستهای پیوندی در #C
1// C# program to sort link list
2// using insertion sort
3using System;
4
5public class LinkedlistIS
6{
7 public node head;
8 public node sorted;
9
10 public class node
11 {
12 public int val;
13 public node next;
14
15 public node(int val)
16 {
17 this.val = val;
18 }
19 }
20
21 void push(int val)
22 {
23 /* allocate node */
24 node newnode = new node(val);
25
26 /* link the old list off the new node */
27 newnode.next = head;
28
29 /* move the head to point to the new node */
30 head = newnode;
31 }
32
33 // function to sort a singly
34 // linked list using insertion sort
35 void insertionSort(node headref)
36 {
37 // Initialize sorted linked list
38 sorted = null;
39 node current = headref;
40
41 // Traverse the given
42 // linked list and insert every
43 // node to sorted
44 while (current != null)
45 {
46 // Store next for next iteration
47 node next = current.next;
48
49 // insert current in sorted linked list
50 sortedInsert(current);
51
52 // Update current
53 current = next;
54 }
55
56 // Update head_ref to point to sorted linked list
57 head = sorted;
58 }
59
60 /*
61 * function to insert a new_node in a list. Note that
62 * this function expects a pointer to head_ref as this
63 * can modify the head of the input linked list
64 * (similar to push())
65 */
66 void sortedInsert(node newnode)
67 {
68 /* Special case for the head end */
69 if (sorted == null || sorted.val >= newnode.val)
70 {
71 newnode.next = sorted;
72 sorted = newnode;
73 }
74 else
75 {
76 node current = sorted;
77
78 /* Locate the node before the point of insertion */
79 while (current.next != null &&
80 current.next.val < newnode.val)
81 {
82 current = current.next;
83 }
84 newnode.next = current.next;
85 current.next = newnode;
86 }
87 }
88
89 /* Function to print linked list */
90 void printlist(node head)
91 {
92 while (head != null)
93 {
94 Console.Write(head.val + " ");
95 head = head.next;
96 }
97 }
98
99 // Driver code
100 public static void Main(String[] args)
101 {
102 LinkedlistIS list = new LinkedlistIS();
103 list.push(5);
104 list.push(20);
105 list.push(4);
106 list.push(3);
107 list.push(30);
108 Console.WriteLine("Linked List before Sorting..");
109 list.printlist(list.head);
110 list.insertionSort(list.head);
111 Console.WriteLine("\nLinkedList After sorting");
112 list.printlist(list.head);
113 }
114}
115
116// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- آموزش برنامهنویسی C++
- مجموعه آموزشهای ریاضیات
- معرفی تکنیکهای مرتبسازی (Sorting Techniques) — ساختار داده و الگوریتم ها
- ۵ الگوریتم مرتبسازی در پایتون — راهنمای کاربردی
- پیچیدگی زمانی الگوریتمهای مرتبسازی با نماد O بزرگ — به زبان ساده
^^