حل مساله کوله پشتی (Knapsack Problem) – به زبان ساده
در این مطلب، روش حل مساله کوله پشتی (Knapsack Problem) بیان و پیادهسازی آن در زبانهای برنامهنویسی گوناگون شامل «سیپلاسپلاس» ++C، «جاوا» (Java)، «پایتون» (Python)، «سیشارپ» (#C) و «پیاچپی» (PHP) انجام شده است. وزن و ارزش n شی داده شده است.
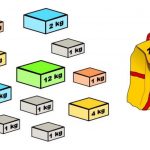
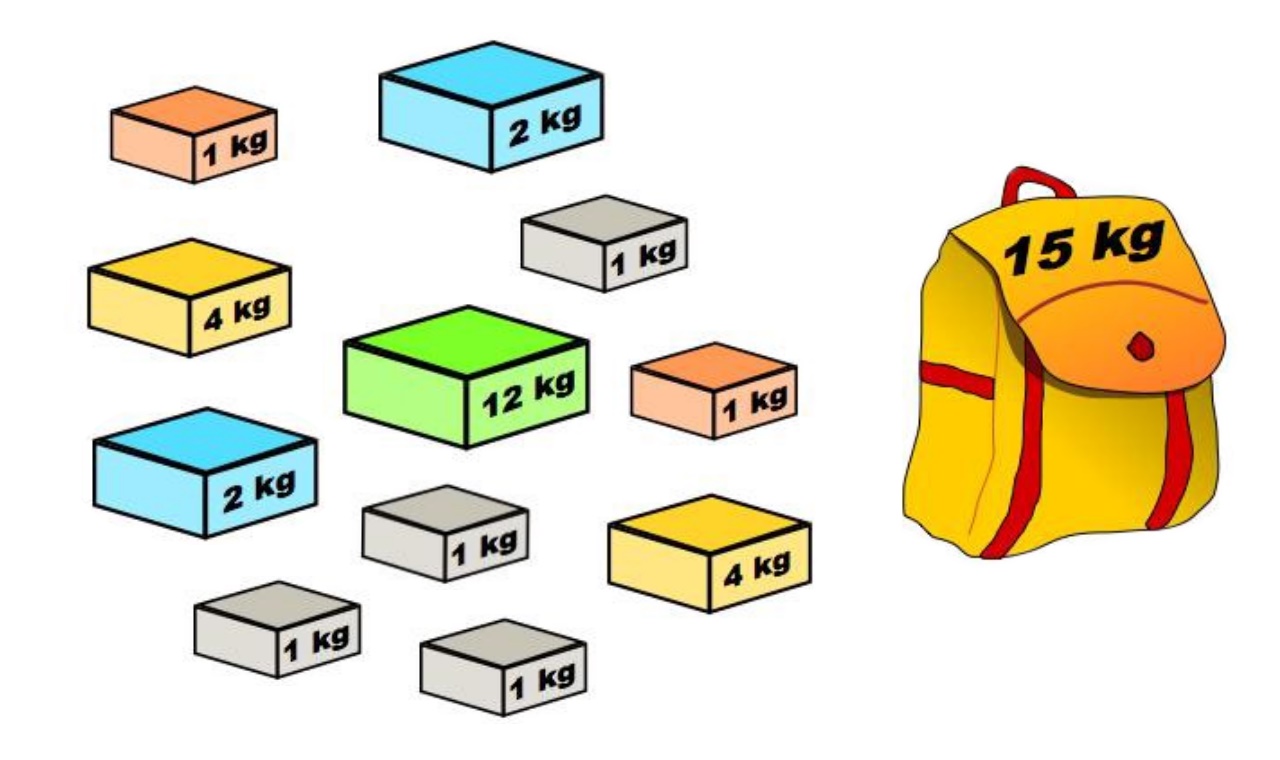
حل مساله کوله پشتی
هدف، قرار دادن این اشیا در کولهپشتی با ظرفیت W به صورتی است که مقدار ارزش بیشینه حاصل شود. به بیان دیگر، دو آرایه صحیح [val[0..n-1 و [wt[0..n-1 وجود دارند که به ترتیب نشانگر مقادیر و وزنهای تخصیص داده شده به n عنصر هستند. همچنین، یک عدد صحیح W نیز داده شده است که ظرفیت کوله پشتی را نشان میدهد.
هدف، پیدا کردن زیرمجموعهای با مقدار بیشینه []val است که در آن، مجموع وزنها کوچکتر یا مساوی W باشد. امکان خورد کردن اشیا وجود ندارد و باید یک شی را به طور کامل انتخاب کرد و یا اصلا انتخاب نکرد. این گونه از مساله کوله پشتی را، «مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰» میگویند.

یک راهکار ساده برای حل این مساله، در نظر گرفتن همه زیر مجموعههای ممکن از اشیا و محاسبه وزن و ارزش کلی هر یک از آنها است. سپس، از میان همه زیرمجموعهها مواردی انتخاب میشوند که وزن کلی آنها کمتر یا مساوی W باشد. در نهایت، از میان زیرمجموعههای دارای وزن کمتر یا مساوی W، زیرمجموعهای با ارزش بیشینه انتخاب میشود.
۱. زیر ساختار بهینه
برای در نظر گرفتن همه عناصر، دو حالت برای هر عنصر وجود دارد. در حالت اول، عنصر در زیر مجموعه بهینه قرار میگیرد و در حالت دوم، عنصر در زیر مجموعه بهینه قرار نمیگیرد. بنابراین، ارزش بیشینهای که میتوان از n عنصر به دست آورد، برابر با بیشینه دو ارزش زیر است:
- ارزش بیشینه حاصل شده از n-1 عنصر و وزن W (به استثنای عنصر nاُم)
- ارزش عنصر nاُم بهعلاوه ارزش بیشینه به دست آمده از n-1 عنصر و وزن W منهای وزن عنصر nاُم
اگر وزن عنصر nاُم بزرگتر از W باشد، این عنصر نمیتواند در کوله پشتی قرار بگیرد و تنها حالت ۱ امکانپذیر است.
۲. زیرمسالههای همپوشان
در ادامه، روش پیادهسازی بازگشتی ساختار بازگشتی بیان شده در بالا ارائه شده است.
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ در ++C
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ در C
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ در جاوا
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ در پایتون
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ در #C
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ در PHP
خروجی قطعه کدهای بالا به صورت زیر است.
220
حل مساله کوله پشتی با برنامهنویسی پویا
شایان ذکر است که تابع بالا، زیرمسالههای مشابه را بارها و بارها حل میکند. برای مثال، زیر درخت بازگشتی (K(1, 1 دو بار محاسبه میشود. پیچیدگی زمانی این روش بازگشتیِ ساده به صورت نمایی و از درجه (O(2n است.
In the following recursion tree, K() refers to knapSack(). The two
parameters indicated in the following recursion tree are n and W.
The recursion tree is for following sample inputs.
wt[] = {1, 1, 1}, W = 2, val[] = {10, 20, 30}
K(3, 2) ---------> K(n, W)
/ \
/ \
K(2,2) K(2,1)
/ \ / \
/ \ / \
K(1,2) K(1,1) K(1,1) K(1,0)
/ \ / \ / \
/ \ / \ / \
K(0,2) K(0,1) K(0,1) K(0,0) K(0,1) K(0,0)
Recursion tree for Knapsack capacity 2 units and 3 items of 1 unit weight.
با توجه به آنکه زیرمسالهها مجددا محاسبه میشوند، این مساله دارای خصوصیت زیرمسالههای همپوشان است. بنابراین، مساله کولهپشتی ۱-۰ دارای هر دو خصوصیت مسائل «برنامهنویسی پویا» (Dynamic Programming | DP) است. همچون دیگر مسائل برنامهنویسی پویا (DP)، میتوان از محاسبه مجدد زیرمسالههای مشابه با ساخت یک آرایه موقت [][]K به صورت پایین به بالا، اجتناب کرد. در ادامه، پیادهسازی راه حل این مساله با استفاده از برنامهنویسی پویا ارائه شده است.
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ با برنامهنویسی پویا در ++C
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ با برنامهنویسی پویا در جاوا
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ با برنامهنویسی پویا در پایتون
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ با برنامه نویسی پویا در #C
حل مساله کوله پشتی ۱-۰ با برنامه نویسی پویا در PHP
خروجی قطعه کدها بالا به صورت زیر است.
220
پیچیدگی زمانی روش بالا از درجه (O(nW است که در آن، n تعداد عناصر و W ظرفیت کولهپشتی است.
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامه نویسی
- آموزش ساختمان دادهها
- مجموعه آموزشهای ساختمان داده و طراحی الگوریتم
- رنگآمیزی گراف به روش حریصانه — به زبان ساده
- الگوریتم دایجسترا (Dijkstra) — از صفر تا صد
- الگوریتم پریم — به زبان ساده
- حل مساله n وزیر با الگوریتم پسگرد (Backtracking) — به زبان ساده
^^










لطفا کد چاپ اقلام انتخابی توسط الگوریتم بعد از اجرا را هم بگذارید یا توضیح دهید.
با سلام. الگوریتم پایتون برای مساله کوله پشتی بسیار آموزنده بود. منتها میخواستم متغیر های تصمیم گیری برداشت اقلام را هم داشته باشم نه اینکه فقط به مقدار تابع هدف نهایی برسم. چکار باید انجام داد؟
“Code Javascript”
الگوریتم کوله پشتی
/ If weight of the nth item is more
// than Knapsack capacity W, then
// this item cannot be included
// in the optimal solution
if (wt[n-1] > W)
return knapSack(W, wt, val, n-1);
// Return the maximum of two cases:
// (1) nth item included
// (2) not included
else return max( val[n-1] + knapSack(W-wt[n-1], wt, val, n-1),
knapSack(W, wt, val, n-1) );
}
var val =new Array (60, 100, 120);
var wt =new Array( 10, 20, 30);
var W = 50;
var n =Math.floor(val.length/(val[0].toString().length));
console.log(knapSack(W, wt, val, n))