مرتب سازی درجی (Insertion Sort) – به زبان ساده
«مرتب سازی درجی» (Insertion Sort) یک الگوریتم مرتبسازی ساده است که روش عملکرد آن مشابه روشی است که افراد کارتهای بازی را در دست خود مرتب میکنند. در این مطلب، به الگوریتم مرتب سازی درجی پرداخته شده و سپس، پیادهسازی آن در زبانهای برنامهنویسی گوناگون، شامل «سیپلاسپلاس» (++C ،(C، «جاوا» (Java)، «پایتون» (Python)، «سیشارپ» (#C) و «پیاچپی» (PHP) انجام شده است.
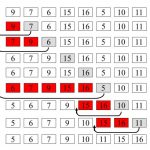
الگوریتم مرتب سازی درجی
//مرتبسازی آرایه []arr با سایز n
- (insertionSort(arr, n
- از i = 1 تا n-1 حلقه بزن
- عنصر [arr[i را انتخاب کن و آن را در توالی مرتب شده [arr[0…i-1 درج کن
مثال اول از مرتب سازی درجی
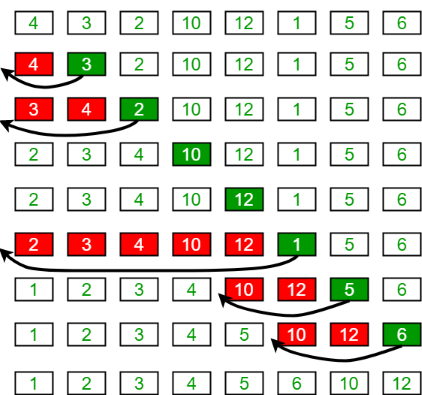
مثال دوم از مرتب سازی درجی
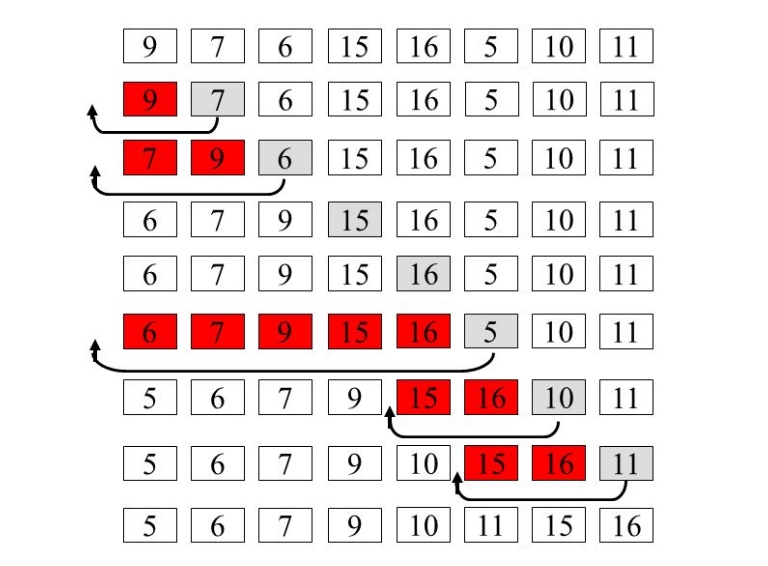
12, 11, 13, 5, 6
از i = 1 (دومین عنصر از آرایه) تا ۴ (آخرین عنصر از آرایه) حلقه بزن.
i = 1. به دلیل آنکه ۱۱ از ۱۲ کوچکتر است، ۱۲ را جا به جا کن و ۱۱ را پیش از ۱۲ درج کن.
i = 2. عدد ۱۳ در جای خود باقی میماند، زیرا همه عناصر [A[0..I-1 کوچکتر از ۱۳ هستند.
11, 12, 13, 5, 6
i = 3. عدد ۵ به آغاز منتقل میشود و همه عناصر دیگر، از ۱۱ تا ۱۳ یک خانه از خانه کنونی خود رو به جلو، جا به جا میشوند.
5, 11, 12, 13, 6
i = 4. عدد ۶ به خانه پس از ۵ منتقل میشود و عناصر از ۱۱ تا ۱۳ به اندازه یک خانه از خانه کنونیشان، به جلو میروند.
5, 6, 11, 12, 13
کد مرتب سازی درجی در ++C
کد مرتب سازی درجی در C
کد مرتب سازی درجی در جاوا
کد مرتب سازی درجی در پایتون
کد مرتب سازی درجی در #C
کد مرتب سازی درجی در PHP
خروجی
خروجی قطعه کدهای بالا، برای آرایه [6, 5, 13, 11, 12] به صورت زیر است.
5 6 11 12 13
پیچیدگی زمانی: (O(n*2
فضای کمکی: (O(1
موارد مرزی (Boundary Cases): مرتب سازی درجی، در صورتی که عناصر دارای ترتیب برعکس باشند، بیشترین زمان اجرا را میبرد. همچنین، در صورتی که عناصر مرتب شده باشند، کمترین زمان اجرا (از درجه n) را خواهد داشت.
مرتبسازی درجا: بله
پایدار: بله
آنلاین: بله
کاربردها: مرتبسازی درجی، هنگامی مورد استفاده قرار میگیرد که تعداد عناصر کم باشد. همچنین، هنگامی که آرایه ورودی تقریبا مرتب شده باشد و تنها چند عنصر در یک آرایه بزرگ در جای نادرست قرار داشته باشند، مرتب سازی درجی گزینه مناسبی خواهد بود.
مرتب سازی درجی دودویی
هنگامی که از جستجوی دودویی برای کاهش تعداد مقایسهها در مرتب سازی درجی استفاده میشود، به آن مرتب سازی درجی دودویی گفته میشود. مرتب سازی درجی دودویی از جستجوی دودویی به منظور پیدا کردن موقعیت مناسب برای درج عناصر انتخاب شده در هر تکرار استفاده میشود.
در درج نرمال، مرتبسازی در بدترین حالت (O(i به طور میانجامد (در iاُمین تکرار). این مقدار را میتوان با استفاده از جستجوی دودویی به (O(logi کاهش داد. به طور کلی، الگوریتم همچنان دارای زمان اجرای (O(n2 است، زیرا مجموعهای از جا به جاییها برای هر درج مورد نیاز است.
پیادهسازی مرتب سازی درجی برای لیستهای پیوندی
در ادامه، پیادهسازی سادهای از مرتب سازی درجی برای لیستهای پیوندی ارائه شده است.
- یک لیست خالی «مرتب شده» (Sorted) (یا «نتیجه» (Result)) بساز.
- لیست داده شده را معکوس کن و اقدامات زیر را برای هر گره انجام بده:
- گره کنونی را به صورت مرتب شده، در لیست «مرتب شده» (Sorted) یا «نتیجه» (Result) قرار بده.
- سر لیست پیوندی داده شده را به سر لیست مرتب شده (یا نتیجه) تغییر بده.
کد مرتب سازی درجی در لیستهای پیوندی در ++C
کد مرتب سازی درجی در لیستهای پیوندی در جاوا
کد مرتب سازی درجی در لیستهای پیوندی در #C
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامهنویسی
- آموزش برنامهنویسی C++
- مجموعه آموزشهای ریاضیات
- معرفی تکنیکهای مرتبسازی (Sorting Techniques) — ساختار داده و الگوریتم ها
- ۵ الگوریتم مرتبسازی در پایتون — راهنمای کاربردی
- پیچیدگی زمانی الگوریتمهای مرتبسازی با نماد O بزرگ — به زبان ساده
^^