الگوریتم رابین کارپ (Rabin–Karp Algorithm) – به زبان ساده
در این مطلب، «الگوریتم رابین کارپ» (Rabin-Karp Algorithm) که برای جستجوی رشته و الگو استفاده میشود، مورد بررسی قرار گرفته و پیادهسازی آن در زبانهای برنامهنویسی گوناگون شامل ++C، «سی» (C)، «جاوا» (Java)، «پایتون» (Python)، «سی شارپ» (#C) و «پیاچپی» (PHP) انجام شده است.


الگوریتم رابین کارپ
فرض میشود که متن [text txt[0..n-1 و الگوی [pat[0..m-1 داده شده است. هدف نوشتن تابع جستجویی (char pat[], char txt[]) است که همه وقوعهای []pat در []txt را چاپ کند.
همچنین، فرض میشود که n > m است. مثال زیر در این راستا قابل توجه است.
Input: txt[] = "THIS IS A TEST TEXT"
pat[] = "TEST"
Output: Pattern found at index 10
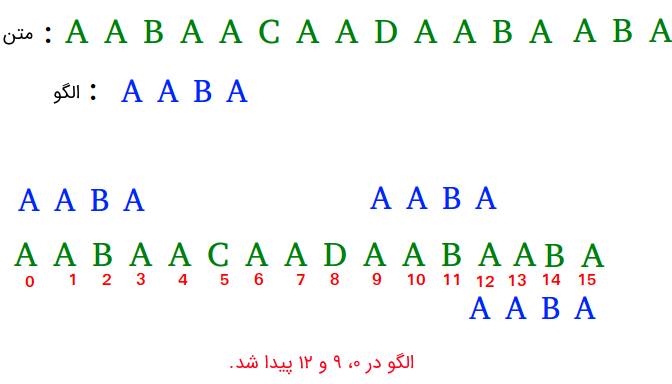
Input: txt[] = "AABAACAADAABAABA"
pat[] = "AABA"
Output: Pattern found at index 0
Pattern found at index 9
Pattern found at index 12
الگوریتم تطبیق الگوی ساده، الگو را به صورت اسلایدی (کشویی) در متن جستجو میکند. پس از هر اسلاید، کاراکترها یکی یکی در قسمت کنونی بررسی میشوند و اگر مطابق با الگو بودند، پرینت میشوند. همچون الگوریتم جستجوی رشته ساده، الگوریتم رابین کارپ نیز الگو را یکی یکی اسلاید میکند. اما بر خلاف الگوریتم ساده، به جای خود الگو و خود متن، الگوریتم رابین کارپ مقدار هش الگو را با مقدار هش زیر رشته کنونی از متن مطابقت میدهد و اگر مقادیر هش با یکدیگر تطبیق داشته باشند، تطبیق کاراکتر به کاراکتر انجام میشود. بنابراین، الگوریتم رابین کارپ نیاز به محاسبه مقادیر هش برای رشتههای زیر دارد.
- خود الگو
- همه زیر رشتههای موجود در متن به طول m
از آنجا که نیاز به محاسبه موثر مقادیر هش برای همه زیررشتهها با اندازه m از متن است، باید یک تابع هش داشت که دارای مشخصاتی باشد که در ادامه بیان شده است. هش در هر جا به جایی (شیفت)، باید به طور موثری بر اساس مقادیر هش کنونی و کاراکتر بعدی در متن قابل محاسبه باشد. در واقع میتوان گفت ([hash(txt[s+1 .. s+m باید به طور کارایی از ([hash(txt[s .. s+m-1 و [txt[s+m قابل محاسبه باشد؛ یعنی [(hash(txt[s+1 .. s+m])= rehash(txt[s+m], hash(txt[s .. s+m-1 و rehash باید عملیات از درجه (O(1 باشد.
تابع هش توصیه شده توسط رابین و کارپ، یک مقدار صحیح را محاسبه میکند. مقدار صحیح برای یک رشته، یک مقدار عددی از رشته است. برای مثال، اگر همه کاراکترهای ممکن از ۱ تا ۱۰ هستند، مقدار عددی "122" برابر با ۱۲۲ خواهد بود. تعداد کاراکترهای ممکن بالاتر از ۱۰ است (عموما ۲۵۶) و طول الگو میتواند بزرگ باشد. بنابراین، مقادیر عددی را نمیتوان به صورت کاربردی به عنوان عدد صحیح ذخیره کرد. بنابراین، مقدار عددی با استفاده از «حساب ماژولار» (Modular Arithmetic) محاسبه میشود تا اطمینان حاصل شود که مقادیر هش را میتوان در یک متغیر صحیح ذخیره کرد (میتواند در کلمات حافظه جا شود). برای هش کردن دوباره (بازهش)، نیاز به خارج کردن قابل توجهترین رقم و افزودن کم اهمیتترین رقم جدید در مقدار هش است. بازهش کردن با استفاده از فرمول زیر انجام میشود.
hash( txt[s+1 .. s+m] ) = ( d ( hash( txt[s .. s+m-1]) – txt[s]*h ) + txt[s + m] ) mod q
hash( txt[s .. s+m-1] ): s مقدار هش در شیفت
hash( txt[s+1 .. s+m] ): (s+1 مقدار هش در شیفت بعدی (یا شیفت
d: تعداد کاراکترها در الفبا
q: یک عدد اول
h: d^(m-1)
عبارت بالا چگونه کار میکند؟
این یک راهکار ریاضیاتی ساده است که در آن، مقدار اعشاری پنجره کنونی بر اساس پنجره پیشین محاسبه میشود. برای مثال، طول الگو ۳ و رشته «۲۳۴۵۶» است. مقدار اولین پنجره (که ۲۳۴ است) برابر با «۲۳۴» محاسبه شده است. برای محاسبه پنجره بعدی یعنی «۳۴۵»، محاسبه ۵+۱۰*(۱۰۰*۲– ۲۳۴) انجام و نتیجه ۳۴۵ حاصل میشود.
الگوریتم رابین کارپ در ++C
الگوریتم رابین کارپ در C
الگوریتم رابین کارپ در جاوا
الگوریتم رابین کارپ در پایتون
الگوریتم رابین کارپ در #C
الگوریتم رابین کارپ در PHP
خروجی قطعه کدهای بالا به صورت زیر است.
Pattern found at index 0 Pattern found at index 10
زمان اجرای میانگین و بهترین حالت برای الگوریتم رابین کارپ از درجه (O(n+m و بدترین حالت از درجه (O(nm است. بدترین حالت از الگوریتم رابین کارپ هنگامی به وقوع میپیوندد که همه کاراکترهای الگو و متن مشابه باشند، به طوری که مقادیر هش همه زیر مجموعههای []txt با مقدار هش []pat تطبیق پیدا کنند. برای مثال، ”pat[] = “AAA و ”txt[] = “AAAAAAA.
اگر نوشته بالا برای شما مفید بوده است، آموزشهای زیر نیز به شما پیشنهاد میشوند:
- مجموعه آموزشهای برنامه نویسی
- آموزش ساختمان دادهها
- مجموعه آموزشهای ساختمان داده و طراحی الگوریتم
- جستجوی الگو (Pattern Searching) — به زبان ساده
- تطبیق رشته فازی در پایتون — راهنمای کاربردی
- کاربردهای هوش مصنوعی در بیوانفورماتیک — به زبان ساده
- متن کاوی (Text Mining) — به زبان ساده
^^